da Sexto B mancano 4 anni
170
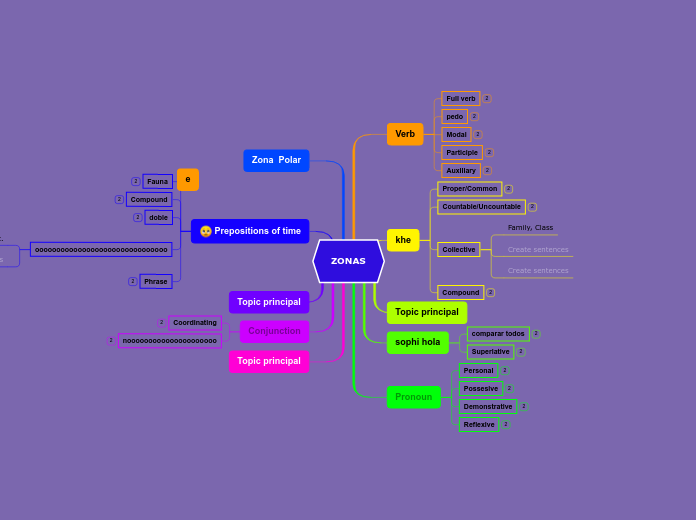
ZONAS
Grammar, Comparison, Prepositions, Modal, Superlative, Compound The text appears to be a collection of various grammatical elements and examples, possibly intended for educational purposes.
da Sexto B mancano 4 anni
170

Più simili a questo
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
A preposition is one of the most exciting parts of grammar. A preposition is used to describe the location of something in relation to something else.
A group of words used with the force of a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
Participle preposition consists of words that end in “ing”.
When a preposition consists of more than one word, it is called double preposition.
Compound preposition consists of two or more words.
When a preposition consists of one word it is called single or simple preposition.
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
A reflexive pronoun ends with ...self or ...selves and refers to another noun or pronoun in the sentence (usually the subject of the sentence). The reflexive pronouns are myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Demonstrative pronouns are used to demonstrate (or indicate). This, that, these, and those are all demonstrative pronouns.
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.