によって ester genovard 6年前.
191
+
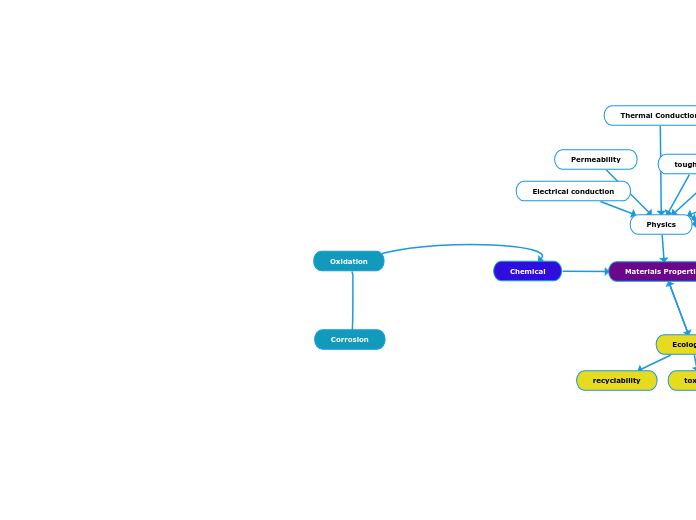
The characteristics of materials can be categorized into chemical, technological, physical, and mechanical properties. Chemical properties involve processes like oxidation, where an atom or compound loses electrons, and corrosion, which leads to material degradation due to environmental interactions.