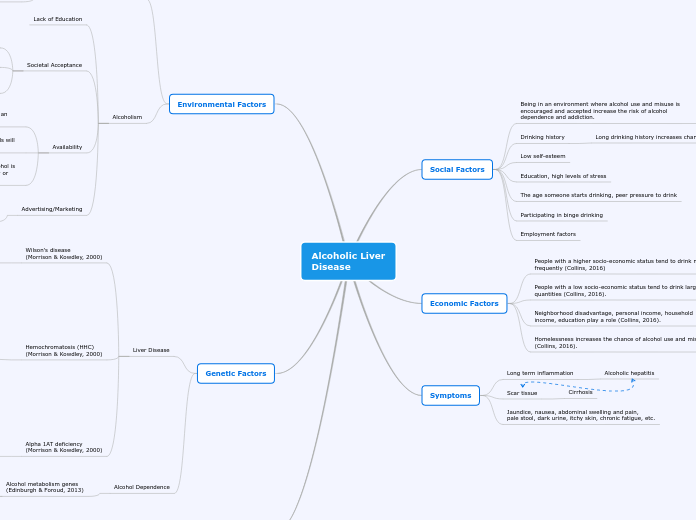
Alcoholic Liver
Disease
Cause
Chronic heavy drinking
Alters liver's ability
to metabolize fats
Fat builds
up in the liver
Genetic Factors
Alcohol Dependence
Alcohol metabolism genes
(Edinburgh & Foroud, 2013)
ALDH2
ADH1B
Alpha 1AT deficiency
(Morrison & Kowdley, 2000)
Mutation in SERPINA1 gene
(Genetics Home Reference, 2020)
Makes alpha 1AT proteins, protects
the body from neutrophil elastase enzyme
Neutrophil elastase released to fight infections, but can attack body tissues when not regulated by alpha 1AT proteins
Hemochromatosis (HHC)
(Morrison & Kowdley, 2000)
Iron deposits collect in
liver and other organs
Type 4
AKA ferroportin disease
Symptoms begin in adulthood;
men between 40-60 and
women after menopause
Mutation in SLC40A1 gene
Makes ferroportin proteins
Transports iron from food into cells
Type 3
Intermediate between type 1 and
type 2; symptoms usually appear
before the age of 30
Mutation in TFR2 gene
(Genetics Home Reference, 2019)
Makes transferrin receptor 2
Helps iron enter liver cells
Type 2
Juvenile onset, if untreated, potential
fatal heart disease is evident by age 30
Mutation in HJV or HAMP gene
(Genetics Home Reference, 2019)
HAMP
Makes hepcidin, inhibits iron absorption when iron levels are too high
HJV
Makes hemojuvelin protein, helps maintain proper iron levels by regulating hepcidin protein.
Type 1
Most common, symptoms begin in
adulthood; men between 40-60
and women after menopause,
Mutation in HFE gene
(Genetic Home Reference, 2019)
Produces surface cell marker for liver and intestinal cells that help detect the amount of iron in the body
Wilson's disease
(Morrison & Kowdley, 2000)
Caused by mutation in
ATP7T gener
Provides instructions to
make copper-transporting ATPase 2
Transports copper from the
liver to other parts of the body
Environmental Factors
Alcoholism
Advertising/Marketing
Alcohol advertisements creates an environment that suggest alcohol consumption and over-consumption are normal activities.
Availability
Underage individuals are more likely to drink when alcohol is freely available to them, either by purchasing it directly or when it's available at parties
The lower the price of alcohol, it's more likely individuals will drink.
The higher number of licensed liquor establishments in an area the more likely individuals are to drink
Societal Acceptance
high profile celebrities, sports star and local role models promoting alcohol with seemingly no adverse effects
Lack of consequences
Media glorifying drinking
Lack of Education
Liver Disease
Pollutants
Lead, mercury, PCB, pesticides, etc.
(American Gastroenterological Association, 2009).
Increases risk for abnormal
liver enzymes
Symptoms
Jaundice, nausea, abdominal swelling and pain,
pale stool, dark urine, itchy skin, chronic fatigue, etc.
Scar tissue
Cirrhosis
Long term inflammation
Alcoholic hepatitis
Economic Factors
Homelessness increases the chance of alcohol use and misuse (Collins, 2016).
Neighborhood disadvantage, personal income, household income, education play a role (Collins, 2016).
People with a low socio-economic status tend to drink larger quantities (Collins, 2016).
People with a higher socio-economic status tend to drink more frequently (Collins, 2016)
Social Factors
Employment factors
Participating in binge drinking
The age someone starts drinking, peer pressure to drink
Education, high levels of stress
Low self-esteem
Drinking history
Long drinking history increases chance of alcohol dependence
Being in an environment where alcohol use and misuse is encouraged and accepted increase the risk of alcohol dependence and addiction.