Chest Pain
Spontaneous pneumothorax
• Sharp pain.
• Localized to one part of the chest.
• Associated with severe dyspnea.
Massive pulmonary embolism
• Sudden onset pain.
• Retrosternal.
• Associated with collapse, dyspnea and cyanosis.
• Pleuritic or angina like pain.
Pain due to dissecting
aneurysm of aorta
• Very severe (tearing).
• Radiate to the back.
Oesophageal spasm
• Retrosternal.
• Come after eating or drinking.
• Associated with Dysphagia.
• Relieved by nitrate.
Disease of cervical
or upper thoracic spine
• Pain is associated with movement
• Radiate from back to front of the chest.
Chest wall pain
• Localised to small area.
• Sharp associated with respiration or movement of shoulders rather than exertion.
• Last for few seconds or to long periods.
Pleuritic chest pain
• Definition: chest pain made worse by inspiration.
• Cause: movement of the inflamed pleural or pericardial surfaces on one another.
• Occur in:
1- Pleurisy . 2- Pericarditis.
• Aggravating and relieving factors:
- Not brought on by exertion but relieved by:
1- Sitting up.
2- Leaning forward.
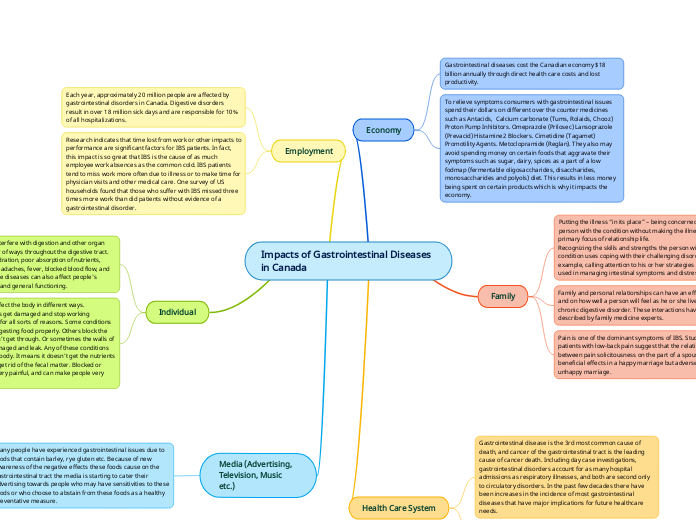
Main topic
CVS
MI
Troponin T and troponin ICreatine kinaseRenal function and electrolytesBlood glucoseFull blood countSerum cholesterolElectrocardiography
dyspnea, sweating, anxiety, nausea, and faintness.
Often no obvious precipitant (not necessarily precipitated by exertion).- Not relieved by rest or nitrates.
Same of angina.
More severe and occur at rest.
usually long (typical duration 30 min or more).
Same of angina
Angina
Treatment
Subtopic
Investigation
Associated symptoms
Aggravating and relieving factors
Aggravating factors:Stress ( as exercise, emotional excitement and cold weather).Relieving factors: A) Rest. B) Sublingual nitrate relief the pain within minutes.
Site and radiation
Retrosternal area or the throat, central and may radiate to the jaw or the arms, rarely travel below umbilicus.
Severity
Graded by New York Heart Association Classification (NYHAC) according to activity to the following:Class I : angina or dyspnea during unusually intense activity.Class II : angina or dyspnea during ordinary activity.Class III : angina or dyspnea during less than ordinary activity.Class IV : angina or dyspnea at rest
Duration
usually short (typical duration 2 – 10 min).
Character
Crushing, heaviness, discomfort or choking sensation.