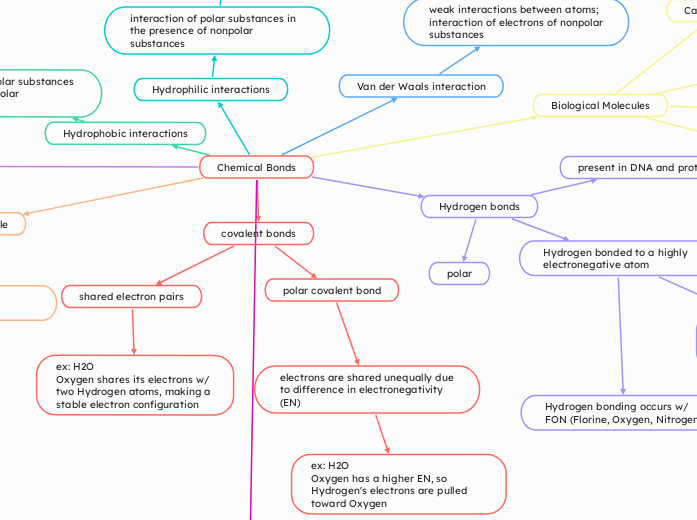
Chemical Bonds
Cell Components
Eukaryotic Cells (Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists)
Nucleus, ER, Golgi, mitochondria, lysosomes, and vaculoes
Vacuoles
Animals: Small vesicles for storage & transport
Plants: Large central vacuole (Stores water, ions, nutrients, maintains pressure)
Lysosomes (Animal Cells)
Break down waste, foreign particles, old organelles
Contain Hydrolytic Enzymes
Mitochondria
ATP production via Cellular Respiration
Own DNA & Ribosomes (Endosymbiotic Theory)
Double membrane (Inner membrane forms cristae)
Golgi Apparatus
Produces lysosomes
Modifies, sorts, packages proteins & lipids
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Smooth ER (Lipid synthesis, Detoxification, Calcium storage)
Rough ER (Ribosomes attached, Protein synthesis & transport)
Nucleus
Nucleolus (rRNA Synthesis) – Ribosome assembly
Chromatin – Genetic storage
Nuclear Envelope – Regulates transport
Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, and cytoskeleton
Cytoplasm & Cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton (Protein Filaments)
Intermediate Filaments – Structural support
Microfilaments (Actin) – Shape, movement
Microtubules (Tubulin) – Transport, spindle fibers
Cytosol (Water, enzymes, dissolved molecules)
Cell Membrane
Cholesterol (in animals)
Carbohydrates (Glycoproteins, Glycolipids) – Cell recognition
Proteins – Transport, signaling
Phospholipid Bilayer (Hydrophobic tails, Hydrophilic heads)
Larger & more complex
Membrane-bound organelles
Prokaryotic Cells (Bacteria & Archaea)
Flagella (Protein-based movement structure)
Nucleoid (Circular DNA, No nucleus)
Plasma Membrane (Phospholipid bilayer)
Ribosomes (Protein + rRNA)
Cell Wall (Peptidoglycan in bacteria)
No membrane-bound organelles
Biological Molecules
Nucleic Acids
Polymer: DNA & RNA
Monomer: Nucleotides (A, T, G, C, U)
Functions: Store genetic information, Direct protein synthesis
Proteins
Polymer: Polypeptides
Monomer: Amino Acids
Structure: Primary, Secondary (α-helix, β-sheet), Tertiary, Quaternary
Functions: Enzymes (catalysts), Transport proteins, Receptors, Structural components (cytoskeleton, extracellular matrix)
Lipids
Phospholipids, Triglycerides, Steroids
Found in: Cell membranes (phospholipid bilayer), Hormones (steroids), Energy stores (fat droplets)
Carbohydrates
Polymer: Polysaccharides (Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose)
Found in: Cell walls (cellulose, peptidoglycan), cell membranes (glycoproteins, glycolipids)
Monomer: Monosaccharides (Glucose, Fructose)
Dipole-Dipole
Ion-Dipole
attractive force between an ion and
a neutral molecule
interaction between polar molecules
Hydrophobic interactions
interaction of nonpolar substances in the presence of polar substances
Hydrophilic interactions
interaction of polar substances in
the presence of nonpolar substances
Water
has high specific heat
w' Hydrogen bonds, helps regulate temperature
adhesion:
interaction with molecules of different substance
ex: allows water to travel up the trees
cohesion:
interaction with molecules
of the same substance.
Van der Waals interaction
weak interactions between atoms;
interaction of electrons of nonpolar substances
Hydrogen bonds
present in DNA and proteins
Hydrogen bonded to a highly
electronegative atom
electronegativity:
Measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons in the context of a chemical bond
Hydrogen bonding occurs w/
FON (Florine, Oxygen, Nitrogen)
polar
ionic bonds
attraction between
charged ions
ex: NaCl
Na has a charge of +1
and Cl has a charge of -1
covalent bonds
polar covalent bond
electrons are shared unequally due to difference in electronegativity (EN)
ex: H2O
Oxygen has a higher EN, so Hydrogen's electrons are pulled toward Oxygen
shared electron pairs
ex: H2O
Oxygen shares its electrons w/
two Hydrogen atoms, making a
stable electron configuration