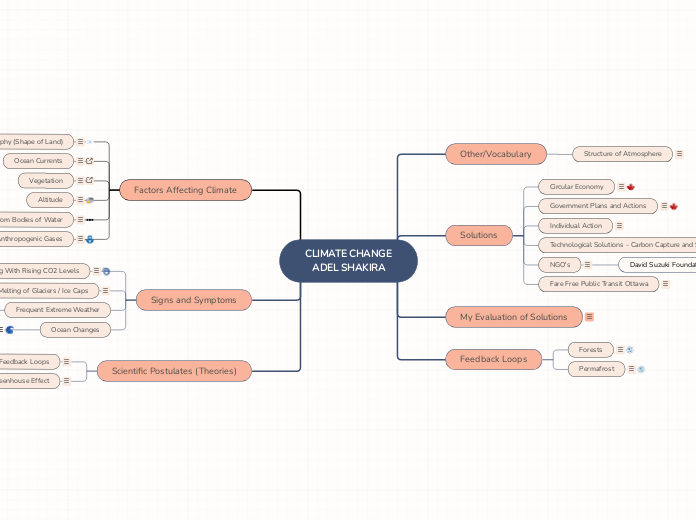
CLIMATE CHANGE
ADEL SHAKIRA
Scientific Postulates (Theories)
Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Effect: The greenhouse effect is a process when gasses in the earth's atmosphere trap the sun's heat. Gasses such as carbon dioxide, absorbs the heat during the day then at night the earth surface cools releasing heat beck into space while maintaining some of the heat from earlier (from the greenhouse gasses). An excess of these GHGs means that too much heat will be trapped, thus warming the overall temperature of the earth by plenty.

Feedback Loops: A feedback loop is the part of a system in which some portion of the systems's output is used for future operations. Feedback loops can either be positive or negative. Positive feedback loops amplify a variable and naturally from its starting state, increasing the effect of the change and produces instability; whereas negative loops are self regulating and reduces the effect of a change. A good example of this would be the increase in temperature would increase the amount of cloud cover as well.
Cloud Cover Feedback Loop: Climate warming -> Increased Eveporation & Cloud Cover -> Decreased Incoming Solar Radiation -> Cooling of the Earth
The result of this negative feedback loop is the decreasing in temperature as the more cloud covering there is, the cooler the earth's surface will become.
Signs and Symptoms
Ocean Changes
Acidification of the Oceans
Acidification of the Oceans: When CO2 is absorbed and dissolved in seawater, the water becomes more acidic and the oceans pH level drops. This change in pH level can have harmful effects on marine life, impacting their chemical communication, reproduction and growth. For example. the building of skeletons in marine life is sensitive to acidity. The chells and skeleton made from calcium continue to dissolve. This can also prevent them from growth a new shell making it harder for creatures who depend on shells to survive.
Frequent Extreme Weather
Hurricanes
Increase in Hurricanes: There are a few factors on why hurricanes are becoming more frequent; some of them being warmer sea temperatures and sea level rise. Not only do warmer sea temperatures increase the amount of hurricanes on average, but it also intensifies the wind speeds and can potentially do more damage. With warmer climates, the sea evaporates much faster producing warm moist air, growing category 4 hurricanes. Another factor is sea level rise, expecting to rise 1-4 feet during this century. This makes it more likely for future coastal storms to form and make coastal storms more devastating.
Melting of Glaciers / Ice Caps
Melting of Glaciers: The overall temperature of the earth has increased significantly over the past decade, and because of this, many of the icecaps have melted. Human activity is the root cause of is excessive melting of the glaciers. Producing greenhouse gasses from agriculture, factories, more of the heat is now trapped within our atmosphere. The consequence of this is the rising sea level causing multiple floods around the globe and a decrease in albedo, resulting in less surface for the UV rays of the sun to reflect back into space.
Rising Temperature Correlating With Rising CO2 Levels
Rising Temperatures Due to CO2: Since carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas (able to absorb UV rays from our sun), it is one of the major factors in global warming. Although carbon dioxide does not hold as much heat as some of the other GHGs, it stays in our atmosphere for longer. The more heat it absorbs the, higher the earth's temperature will become, as the heat will be trapped within our system.
Factors Affecting Climate
Anthropogenic Gases
Anthropogenic Gases: Anthropogenic gasses are essentially human-made gasses emitted from human activities. This includes the burning of fossil fuels, agriculture, transportation and so on. The major greenhouse gasses are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and other synthetic chemicals.
- Carbon dioxide is created from the combustion of fossil fuels and other emission sources.
- Methane comes from coal mining, natural gas production, waste decomposition agriculture etc.
- Nitrous oxide is emitted during agricultural and industrial. activities as well as combustion of solid waste and fossil fuels.
Distance From Bodies of Water
Distance from Bodies of Water: Although landmasses heat up more quickly than water, it loses heat quicker as well. The oceans retain longer than land, meaning that coastal locations tend to be cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter than places with an area with a continental climate. For example, PEI's climate does not fluctuate nearly as much as Alberta throughout the seasons due to the waters retaining heat.
Altitude
Altitude: As elevation increases, the weather gets colder and increasingly harder (intense weathering and wind), contrarily, as elevation decreases the weather will be warmer and more humid. There will also be less air above you thus the pressure decreases. For example, when you board a plane, the windows are not as cold; mid-flight the windows are noticeably colder than before you took off. This is because of the thinning of the atmosphere. the higher you go, the total heat content of the air decreases.
Vegetation
Vegetation: Vegetation can affect climate and weather patterns due to the release of water vapour during photosynthesis. Conversely, climate and temperatures can decide whether or not the specific type of vegetation can survive in the climate. The vapour that the plant release alters the amount of potential cloud formation in the sky. In addition to altering cloud formation, they can also lower surface and air temperature by providing shade; cooling the area by around 11-25°C.
Ocean Currents
Ocean Currents: Water retains heat better than land, which is why maritime climates tend to have winter temperatures similar to their summer temperatures. Ocean currents distribute heat around the globe by transporting warm water in a continuous flow by surface winds. The direction of ocean currents can also be affected by temperature, salinity gradients, earth's rotation and tides. Major current systems typically flow clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere in circular patterns that go around the coastlines.
Topography (Shape of Land)
Topography: Describes the physical features of the land in a specific region. It can influence precipitation and temperature. For example, if an area of water is close to a body of water, it tends to have a milder climate than an area surrounded by mountains which tend to have more extreme weather. We see this effect in mountains ranges as one side tends to have more vegetation than the opposing side. The mountain acts as a barrier to air and moisture, leaving one side dry and the other side suitable for vegetation. This is called the orographic effect and this can alter the weather conditions in a region.
Orographic Diagram:

Feedback Loops
Permafrost
Permafrost: Permafrost is when a layer of the earth is frozen permanently all year round. Any temperatures 0°C or lower for at least two years will be considered permafrost. Thawing permafrost has dramatic impacts on our planet because when permafrost is frozen plant material called organic carbon cannot decompose; as it melts, microbes begin decomposing this material. This process releases greenhouse gasses such as carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere.
Permafrost Melt: Tempurature Rises -> Permafrost Thaws -> More Microbial Activity -> CO2 and Methane ->
By implementing good choices another feedback loop arises. We can then support a sustainable future by curbing fossil fuel use and regreening the earth. For permafrost, the less warming we create, the less carbon dioxide and methane will be released into the atmosphere, which means the overall temperature will drop and permafrost will stay frozen.
Forests
Forests: Forest regulates the ecosystems and also play a crucial role in climate change. For example, 1.7 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide are being absorbed by the Amazon rainforest. This is important because of the effects that carbon has on the role of our atmosphere. This process can be shown through a feedback loop:
CO2 Feedback Loop: More CO2 -> Temperature Rises -> Hotter, Drier -> Droughts, Fire, Insects ->
My Evaluation of Solutions
My Evaluation of Solutions: Out of all the solutions I have covered, the most effective and most appealing to me are both the government's action plans and the individual actions. The rest fall into place as the citizens help come up with solutions and the government is able to implement these changes by directing the money towards climate change. I believe that in numbers, changing our lifestyle habits will be able to decrease usage of natural resources which otherwise would continue depleting. This is where things like the circular economy and other solutions to reuse resources are implemented.
The government has multiple plans in order to reduce the amount of fossil fuel emissions such as net zero emissions, investing in carbon capture and storage technology and switching from oil and fossil fuel to cleaner fuels. The problem with that is not only the cost, but how Canada's economy is heavily reliant on the export of natural resources for their GDP. Another potential problem with carbon capture is how using the captured carbon in geological formations may defeat the purpose of trying to contain it in the first place. Once the oil is harvested again it will produce more CO2 than what was originally emitted.
Although citizen's opinions are taken into account when making government decisions, in some instances the government will make empty pledges about the action they promise to take. Some citizens notice that it's all planning and no action, but this is where NGOs like the David Suzuki Foundation come into play. Organizations like these hold the government accountable, making sure that they follow through with their plans. In the end, the government and citizens come hand in hand with making an impact in climate change.
Solutions
Fare Free Public Transit Ottawa
Free Fare Public Transit Ottawa: Although one might think that having free public transit would be increasing the amount of fossil fuel emissions, it is the opposite. If everyone were to use their own vehicle, that would be more gas used than if indivuals chose to ride in a public vehicle simultaneously, reducing the carbon footprint by a long shot. If a single person, commuting alone by car, who switches to a 20 mile round trip public transportation, they can reduce their annual CO2 emissions by 4,800 pounds per year. Not only does this solution give the choice to citizens looking to decrease their carbon footprint, but it is also vital to the health and quality to Canada's citizens.
More pros to this system includes:
- higher densities allowing closer spacing in houses as people will not need extensive driveways for vehicles
- Is estimated to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 37 metric tons annually
- Provides an affordable alternative to driving as households that take public transportation save up to $6,251 every year
- Provides an option to those looking to reduce their energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions
Overall, the free fare transit plan is a convenient way to reduce emissions while also having a system where everyone has access to free transportation. There will be less personal vehicles on highways, meaning less traffic and the more space we are able to conserve in terms of wildlife and national park reserves.
NGO's
NGO's: An NGO stands for non-governmental organization and is a non-profit organization that operates independently without any funds from the government. The purpose of these organizations is to promote and address a social or political issue.
David Suzuki Foundation
David Suzuki Foundation: The David Suzuki foundation implements strategies to ensure federal, provincal and territorial governments take action on climate change. They are taking action on climate plan to reduce emissions by 60% by the year 2030 while also holding the government accountable for the efforts they promise to take. On top of that they plan to end all fossil fuels subsides. Meaning that the oil and fossil fuel sector will no longer be funded by the government in the form of subsides.
Technological Solutions - Carbon Capture and Storage
Technological Solutions - Carbon Capture: Although many are employing alternatives for fossil fuels, it is still one of the largest energy sources out there. In order to combat the amount of emissions being released into the air, carbon capture technology will be able to prevent the amount of greenhouse gasses from reaching our atmosphere.
With the use of carbon capture technology, we can capture more than 90 percent of carbon dioxide produced from power plants and industrial facilities. The used carbon can also be put into productive use in enhanced oil recovery and the manufacture of fuels, building materials or for geological formations.
The process of the carbon being used for geological formations includes a three step process of capturing the carbon, the CO2 is separated from other gasses produced in industrial processes such as those at coal and natural gas fired generation plants or steel or cement factories. Then the carbon is then compressed and transported from pipelines, road transport or ships. The last step is to inject the carbon into rock formations underground or for permanent storage.
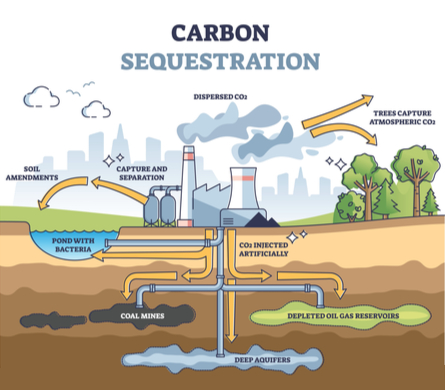
This solution is absolutely necessary in order to achieve Canada's plan of net zero emissions as Canada's economy is not planning to eliminate oil and natural gas extraction altogether. This will also benefit the balance of emissions from vehicles, energy sources and factory pollution.
Individual Action
Induvidual Action: Citizen action on climate change can come in the form of personal choice and habits such as diet, household energy use, consumption of goods, travel habits and many more. We can also take action by engaging in local and political issues surrounding climate change.
An example of this could be choosing sustainable fashion over fast fashion. When the prices of fast fashion is cheap, consumers tend to purchase items they would use once or twice before disposing of it. Buying from brand and companies that support eco-friendly production would typically be more on the pricey side, but this also leaves room for the consumer to think about whether to not this item is really needed - similar to an investment.

Direct result of fast fashion
To be more involved locally and be more informed, there are options to participate in local non-profit organization activities such as park clean ups, protesting on climate change, and participating in projects to improve the overall wellbeing of the environment.
Overall, I think that small changes in habits, if repeatedly done, can have a massive impact on our environment when collectively done. Things such as taking shorter showers will decrease the overall consumption of water over time. So in conclusion, individual action is just as important as any other major steps we are taking to combat climate change.
Government Plans and Actions
Government Plans and Actions: Canada's government has plans and policies that are being implemented to build resilience and prevent climate change. On their site, they have mentioned that they plan to reduce emissions by making energy in homes more cost efficient, investing in cleaner transportation, using alternatives to oil and gas and more. We are now seeing this being implemented in transportation as renewable energy sources are being promoted. Ethanol, renewable gasoline, biodiesel and renewable diesel are only some of the sources they are replacing fossil fuels with.
One of the climate plans the government has listed on their site was "net zero emissions by 2050". The initial goal is to transition into an economy that emits no greenhouse gasses; one that employs technologies that capture carbon before it reaches the atmosphere, thus, creating greenhouse emissions.
The actions that the government is taking are crucial to decrease the effects of climate change, as the less greenhouse gasses, the more we can continue to keep the world safe and liveable for future generations.
Circular Economy
Circular Economy: Different from a linear economy, a circular economy recovers resources used by reusing, repairing refurbishing products and materials. A linear economy would have a supply of raw materials that are processed into a product that is thrown away after use. The structure of a circular economy ensures that all materials are being used to their full potential.
There are many real-life examples of this in businesses such as start-ups, semi-public organizations and more. A great example of this would be the start-up product/company Smartcrusher; which focuses on reducing carbon dioxide emissions from concrete production. Although concrete can last for hundreds of years, every kilogram of concrete produces one kilogram of CO2 emissions. This is three times the amount of CO2 all aircraft produce. Smart crusher is a device that separates unused cement stone from concrete rubble. The cement stone can be used in concert production and thus saves cement and CO2 emissions.

I say that this solution is an effective one for businesses to implement not only because of its ability to reduce waste and emissions but because it is able to save money in the long run. Even if it costs more to implement these systems, in the future you will be salvaging plenty of materials. For example, if you were to turn your pulp and paper waste into renewable plastics or textiles, there will then be a new life for the resources that may have ended up in the landfill.
Other/Vocabulary
Structure of Atmosphere
Structure of the Atmosphere: Within our atmosphere, there are many different layers as follows:
Troposphere
This layer is the closest layer to the planet and contains the largest percentage of the mass of the total atmosphere. It also holds the most water vapour in our atmosphere with around 99% where all the weathering occurs - snow, rain, hail etc.
Stratosphere
This extends upwards from the tropopause to about 50 km. This part contains much of the ozone in the atmosphere. The increase in temperature in this layer occurs because of the absorption of ultraviolet radiation from the sun by the ozone.
Mesosphere
The region above the stratosphere is called the mesosphere. The temperatures here decrease with height, reaching a minimum of -90°C at the mesopause.
Thermosphere
the thermosphere lues above the mesopause and this area increase in temperature with height. The temperature increase is caused by the absorption of energetic ultraviolet rays from the sun.
Exosphere
This region is about 500 km the thermosphere is called the exosphere. It is made primarily of oxygen and hydrogen atoms.