によって Laura Northcutt 4年前.
1033
Confucianism
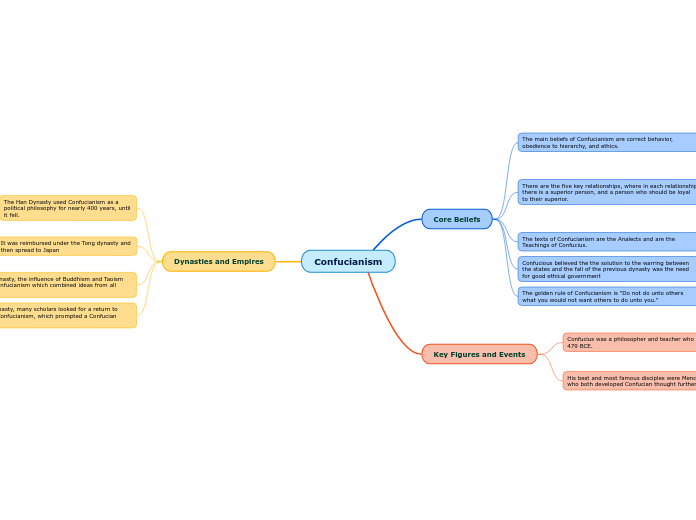
Confucianism, founded by Confucius, emphasizes ethics, good behavior, and moral character. His disciples, Mencius and Xunzi, further developed his teachings, which were compiled into texts like Lunyu.
によって Laura Northcutt 4年前.
1033

もっと見る
Confucian schools were established to teach Confucian ethics.
They would then have to pass the civil service exam.
This emphasizes the Confucian belief of ancestor worship.
This involves obeying their wishes and taking care of them when they are old.