によって Clodagh Stevens 5年前.
223
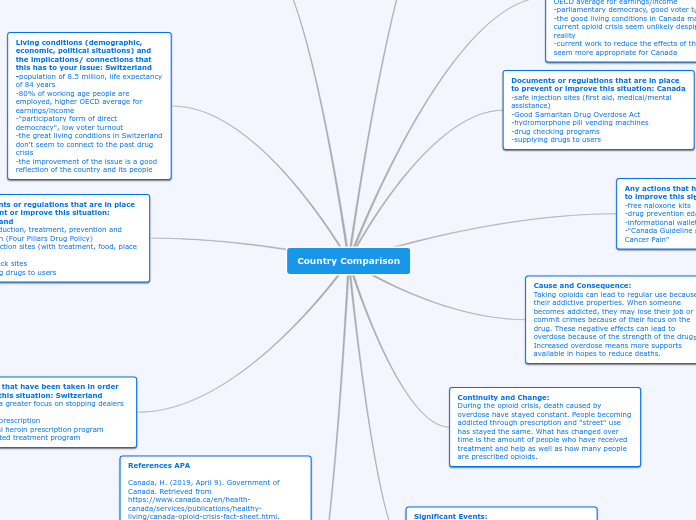
Country Comparison
Both Canada and Switzerland have implemented various measures to address the opioid crisis, recognizing its severe impact on public health and social stability. Canada has focused on distributing free naloxone kits, providing drug prevention education in schools, and disseminating informational wallet cards.