によって Nicholas Casson 4年前.
280
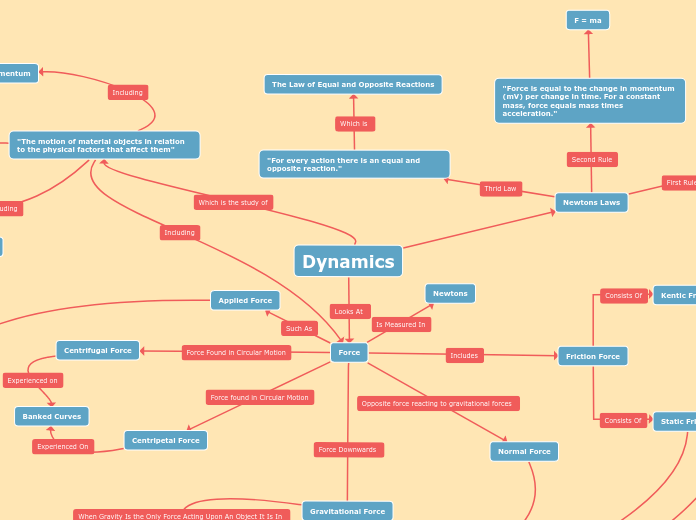
Dynamics
The principles of mechanics revolve around the behaviors and interactions of objects under various forces. Newton's laws provide a foundational understanding of these interactions, outlining how objects remain in motion or at rest unless acted upon by external forces and how every action has an equal and opposite reaction.