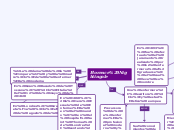
EDUCACIÓN RURAL Y EDUCACIÓN URBANA
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
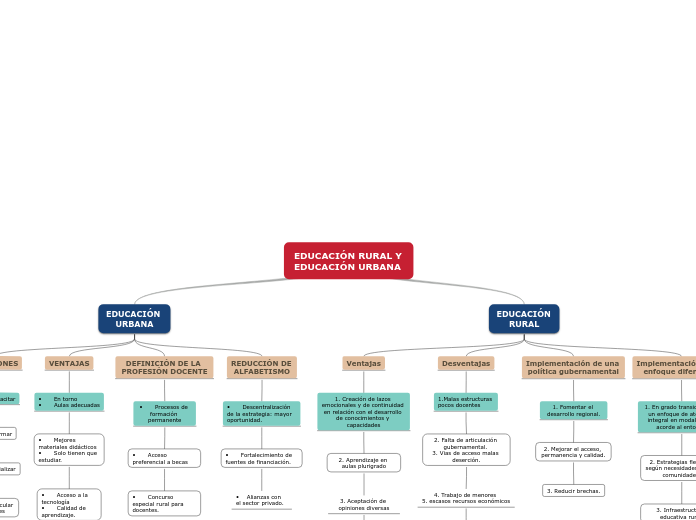
EDUCACIÓN RURAL
Implementación de un enfoque diferencial
1. En grado transición con un enfoque de atención integral en modalidades acorde al entorno.
2. Estrategias flexibles según necesidades de las comunidades.
3. Infraestructura educativa rural.
Implementación de una política gubernamental
1. Fomentar el desarrollo regional.
2. Mejorar el acceso, permanencia y calidad.
3. Reducir brechas.
Desventajas
1.Malas estructuras
pocos docentes
2. Falta de articulación gubernamental.
3. Vias de acceso malas
deserción.
4. Trabajo de menores
5. escasos recursos económicos
6. no material didáctico.
7. No hay acceso a la tecnología
Ventajas
1. Creación de lazos emocionales y de continuidad en relación con el desarrollo de conocimientos y capacidades
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
EDUCACIÓN RURAL.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
2. Aprendizaje en aulas plurigrado
3. Aceptación de opiniones diversas
4. Docente con autonomía el uso y gestión
5. Numero reducido de alumnos.
EDUCACIÓN URBANA
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
REDUCCIÓN DE ALFABETISMO
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
• Descentralización de la estrategia: mayor oportunidad.
Point of view
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view. Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: I can't get the poetry of the trees,' he said. She nodded. Don't worry,' she said. You will someday. He believed her.' (Paterson, 4. 24)
• Fortalecimiento de fuentes de financiación.
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
• Alianzas con el sector privado.
DEFINICIÓN DE LA PROFESIÓN DOCENTE
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
• Procesos de formación permanente
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
• Acceso preferencial a becas
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
• Concurso especial rural para docentes.
VENTAJAS
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
• En torno
• Aulas adecuadas
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
• Mejores materiales didácticos
• Solo tienen que estudiar.
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of viewSecond person point of viewThird person point of viewOmniscient point of view
• Acceso a la tecnología
• Calidad de aprendizaje.
• La familia acompaña al estudiante.
• Cuentan con afecto
• Acceso a la alimentación, salud y socialización.
FUNCIONES
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
• Capacitar
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
EDUCACIÓN URBANA.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
• Formar
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
• Socializar
• Vincular valores
• Estructurar conocimientos