Experiential Education & Field-Based Teaching and Learning:
Principles and Practices
Jay Roberts, Ph.D.
Earlham College
How does this inform our curriculum, our pedagogical designs moving forward?
Examples of how you have experienced this (or not?) at CC?
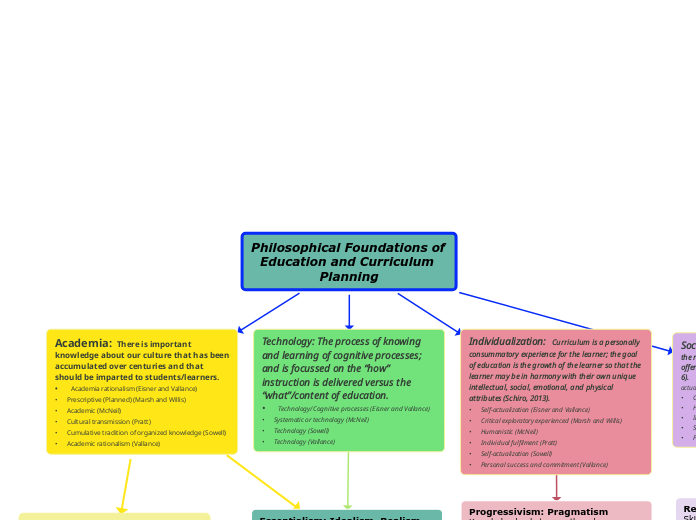
Defining Experiential Education:
What is Experiential Education?
AEE's Principles
The design of the learning experience includes the possibility to learn from natural consequences, mistakes and successes.
The educator's primary roles include setting suitable experiences, posing problems, setting boundaries, supporting learners, insuring physical and emotional safety, and facilitating the learning process.
The educator and learner may experience success, failure, adventure, risk-taking and uncertainty, because the outcomes of experience cannot totally be predicted.
Learners are engaged intellectually, emotionally, socially, soulfully and/or physically. This involvement produces a perception that the learning task is authentic.
Throughout the educational process, the learner is actively engaged in posing questions, investigating, experimenting, being curious, solving problems, assuming responsibility, being creative, and constructing meaning.
Experiences are structured to require the learner to take initiative, make decisions and be accountable for results.
Experiential learning occurs when carefully chosen experiences are supported by reflection, critical analysis and synthesis.
Experiential education is a philosophy that informs many methodologies in which educators purposefully engage with learners in direct experience and focused reflection in order to increase knowledge, develop skills, clarify values, and develop people's capacity to contribute to their communities.
The Experiential Learning Cycle
Is it experiential learning?
Pop Quiz!
A student initiated research project
An internship
Small group discussions in class
A student produced play or drama production
A computer-based game/simulation to learn/practice classroom content
A study tour trip to France
English students role-playing a scene from a novel
A chemistry lab
A student volunteers at the local food pantry
A lacrosse coach has students run an offense vs defense scrimmage
Core Methodologies
Discussion
Groups of 4
Problem-Based Learning
Team Magic Bus
University of Oregon Sustainable Cities Initiative
University of Virginia Bay Game
Cooperative Jigsaw
As a group-- what further questions or points of discussion do you have at this point?
Teach your methodology
Expert Groups
Discuss pro's and con's of this methodology
Come up with ideas or examples of this methodology in practice
Review handout and definition for your methodology
Home Groups
Which are you less familiar with and/or have questions about?
Which have you employed and how?
Review list of experiential methodologies
EE and Terms
Inquiry-Based Learning
Place-Based Learning
Cooperative Learning
Game-Based Learning
Project or Problem-Based Learning
Community-Based Learning
Service Learning
Final Design Thoughts
Groups of 3
Curriculum Workshop
Tweaking an existing course?
Dream course?
Design challenge?
Fail fast, fail forward
Think about assessment in the design itself
Go bigger!
BHAG
Program level, unit level, institution-wide
An entire unit of a class; a semester project
Keep it simple!
Don't do more; do different
One class, one experience
Just Get Started
Scales
Macro
Meso
Micro
Introduction to Experiential Design
Integration
What is extraneous? What could be amplified?
Are the feedback and assessment strategies consistent with the learning goals and activities?
Are the learning activities consistent with the learning goals?
Teaching and Learning Activities
Integrative Learning
PBL
CBL
Active Learning
Feedback and Assessment
Forward-Looking Assessment
Constructed to determine whether students are ready for some future activity, after the current period of learning is over
Backward-Looking Assessment
Constructed to determine whether students "got" the material
"A student portfolio is a compilation of academic work and other forms of educational evidence assembled for the purpose of (1) evaluating coursework quality, learning progress, and academic achievement; (2) determining whether students have met learning standards or other academic requirements for courses, grade-level promotion, and graduation; (3) helping students reflect on their academic goals and progress as learners; and (4) creating a lasting archive of academic work products, accomplishments, and other documentation."
http://edglossary.org/portfolio/
Capstone
Reflection-oriented/transfer
Project-based (multiple classes)
Development within a course
Skill, competency specific
Digital Dumping Ground
Authentic Assessment (Wiggins and McTighe)
Allows opportunities to rehearse, practice, get feedback, and refine
Discrete lessons are made meaningful toward mastery
Asks students to integrate across KSA's (not isolate)
Replicates challenging "real life" situations
Asks students to "do" the subject
Requires judgement and innovation
Realistically contextualized
What will the students have to do, to demonstrate that they have achieved the learning goals?
"A rubric is a scoring tool that explicitly represents the performance expectations for an assignment or piece of work. A rubric divides the assigned work into component parts and provides clear descriptions of the characteristics of the work associated with each component, at varying levels of mastery."
https://www.cmu.edu/teaching/designteach/teach/rubrics.html
"Formative assessment refers to a wide variety of methods that teachers use to conduct in-process evaluations of student comprehension, learning needs, and academic progress during a lesson, unit, or course. ... In other words, formative assessments are for learning, while summative assessments are of learning."
www.edglossary.org
"Assessment is a process by which information is obtained relative to some known objective or goal. Assessment is a broad term that includes testing. A test is a special form of assessment. Tests are assessments made under contrived circumstances especially so that they may be administered. In other words, all tests are assessments, but not all assessments are tests."
http://www.adprima.com/measurement.htm
How do we know what we are doing is working?
Learning Goals
Significant Learning
"Significant Learning" as opposed to "Understand and Remember"
Pairs: EELDRC how to tie a shoe...
CONNECT: On-ramping with other content, experiences
REVIEW: Multiple opportunities for feedback and reflection
DEMONSTRATE: Practice through content
LABEL: Punctuated direct instruction
EXPERIENCE: Experience Before Label!
ENROLL: The importance of framing
Can happen at any scale: micro, meso, macro
Two Basic Design Frames to Consider
Fink- Integrated Course Design
Integrated Course Design
EELDRC
Key General Principles
Chunking and stages
IBFVTNOJBLKFJ
Design for Significant/High Impact Learning
Go Big! Go Small!
UbD
What are the enduring understandings?
Trivial Trap
Crawford's "Build-A-Bear" Analogy
Grading Trap
Activity Trap
No "one best way"
JFK LBJ ON TV FBI
Common Characteristics of EE
Authenticity-- of product/task and audience
Risk
"Fail Fast" or "Fail Forward" orientation
"Messy"
Ambiguity, unpredictability, and uncertainty
John Dewey's "Indeterminate Situation"
Experience before Label
Experiential Learning Cycle
Day Two!
Warm-Ups
Paired share progression
A memorable edu design moment
Define EE?
Something from yesterday
Dinner
Overview
Design and EE
Facilitation and Experiential Education
Principles of Facilitation
Q and A/Discussion
Group Dynamics and Management
Interventions
Be prepared for failure
Grit, adaptation, resilience
Fail forward
What are your outcomes?
Return to First Principles
Models
Peer/group feedback
Plus, Delta (Roses and Thorns, Apples and Onions)
Gems and Opportunities
Continue, Start, Stop
Differentiation
Head Toward Trouble
Waterline Model
Stages
Processing
Multi-modal Pt 2
Gallery walks
Social media!
Digital Storytelling
POL's
Meta-assignments
Written
Verbal/Oral
Interpersonal
Intrapersonal
Cognitive
Kindling, big logs, and progressions
What? So What? Now What?
Iterative feedback and formative assessment
On-going (not just at end of experience)
Framing and Tone Setting
Social Context
Collaboration skills
Full-Value Contracts
Relationships 101
Are they ready?
Gradient
Zone of Proximal Development
Set clear expectations
Make outcomes relevant and overt
Sense of invitation
The Real Work
It may be that when we no longer know what to do
we have come to our real work,
and that when we no longer know which way to go
we have come to our real journey.
The mind that is not baffled is not employed.
The impeded stream is the one that sings.
~ Wendell Berry
Final Reflections and Takeaways
Meeting the Challenge?
Purpose Learning
Stanford d.school
Transformation
"We all know or sense that the academy today is in the throes of transformation. The knowledge, skills, and values in which students should be educated; the intellectual landscape of the disciplines and degrees; the ways in which educational institutions are organized; the funding of teaching, learning, and research-- all of this promises to be profoundly different in 20 years. The forces of change have resulted partly from our own inertia, partly from consequences of our success, and partly from broad political, market, and technological developments not of our making. The question is not whether the academy will be changed, but how." (Scobey, 2012)
A World of "Wicked" Problems
Wicked Problems
Does our current educational system prepare students to work in these kinds of contexts?
as
"These pressures are disruptive because to this point we have funded and structured our institutions as if the formal curriculum were the center of learning, whereas we have supported the experiential co-curriculum (and a handful of anomalous courses, such as first-year seminars) largely on the margins, even as they often serve as the poster children for the institutions’ sense of mission, values, and brand. All of us in higher education need to ask ourselves: Can we continue to operate on the assumption that the formal curriculum is the center of the undergraduate experience?" (Bass, 2012)
"By using the phrase “disrupting ourselves” ... I am asserting that one key source of disruption in higher education is coming not from the outside but from our own practices, from the growing body of experiential modes of learning, moving from margin to center, and proving to be critical and powerful in the overall quality and meaning of the undergraduate experience. As a result, at colleges and universities we are running headlong into our own structures, into the way we do business." (Bass, 2012)
Time stress
Uncertain, unclear data
High potential for unforeseen consequences
Dispersed responsibility and power
Contested and Complex
Racism, Hyper-Nationalism, Xenophobia
The world is full of complex, unscripted problems where the answers are not immediately known and the consequences matter.
"Easily" solvable?
Solvable by any one discipline?
Water Rights
Terrorism
Zika/Global Health
Income Inequality
Climate Change
UNENGAGED?
Just over one-third of college faculty surveyed in 2007 strongly agreed that their campus actively promotes awareness of US or global social, political, and economic issues.
Only one-third of college students surveyed strongly agreed that their college education resulted in increased civic capacities.
ANEMIC SENSE OF PUBLIC SERVICE?
"In survey after survey, employers seem to agree that the skill they most want in future workers is adaptability. Those who hire complain that they often find today’s college graduates lacking in interpersonal skills, problem solving, effective written and oral communication skills, teamwork, and the ability to think critically and analytically."
From: http://chronicle.com/blogs/next/2012/09/12/skills-gap-employers-and-colleges-point-fingers-at-each-other/
UNPREPARED?
Experiential Education: Why It Matters in a World of Seismic Disruption
Socio-Economic Disruptors
Generation "Z"
Ages 5-18
"Likes"
Personal connections
Small class sizes
Professional opportunity
Real world experience
Hands-on learning
Affordability and Attendance
The credit crisis (student loan debt in US exceeds total credit card debt for first time in 2012)
"In 2009, spending by Americans for post-secondary education totaled $461 billion, an amount 42% greater than in 2000, after accounting for inflation. This $461 billion is the equivalent of 3.3% of total U.S. gross domestic product (GDP) and an amount greater than the total GDP of countries such as Sweden, Norway and Portugal."
From: http://www.cnn.com/2011/12/02/opinion/vedder-college-costs/index.html
College Attendance: "In 1960, 392,000 students earned bachelor degrees. By 2007 that number had nearly quadrupled to 1.52 million."(Ferrall, 2011)
Global Recession
College-to-Career focus
Market, ROI, Outcomes, Accountability, Value Proposition
"Neo-Liberal" Academy
Epistemological Disruptors
American Academy for the Advancement of Science:
“As biology faculty, we need to put the “depth versus breadth” debate behind us. It is true today, and will be even more so in the future, that faculty cannot pack everything known in the life sciences into one or two survey courses. The advances and breakthroughs in the understanding of living systems cannot be covered in a classroom or a textbook. They cannot even be covered in the curriculum of life sciences majors. A more tenable approach is to recast the focus of biology courses and curricula on the conceptual framework on which the science itself is built and from which discoveries emerge. Such a focus is increasingly interdisciplinary, demands quantitative competency, and requires the instructor to use facts judiciously as a means of illustrating concepts rather than as items to be memorized in isolation.
The time has come for all biology faculty, but particularly those of us who teach undergraduates, to change the way we think about teaching and begin to develop a coordinated and sustainable plan for implementing sound principles of teaching and learning." (2009)
National Academies (2005). "Facilitating Interdisciplinary Research." Four drivers...
The need to produce revolutionary insights and generative technologies
The need to solve social problems
The desire to explore problems and questions that are not confined to a single discipline
Inherent complexity of nature and society
Emerging Neuroscience of Learning
Importance of student-centered exploration FIRST
STANFORD STUDY
"The study involved 28 undergraduate and graduate students as participants, none of whom had studied neuroscience. After being given an initial test, half of the group read about the neuroscience of vision, while the others worked with BrainExplorer. When tested after those respective lessons, the performance of participants who used BrainExplorer increased significantly more – 30 percent – than those who had read the text.
Next the researchers had each of the two groups do the other learning activity: Those who had used BrainExplorer read the text, while those who had read the text used BrainExplorer. All the participants then took another test, and the findings revealed a 25-percent increase in performance when open-ended exploration came before text study rather than after it. (A follow-up study showed identical results for video classes instead of text.)
“We are showing that exploration, inquiry and problem solving are not just ‘nice to have’ things in classrooms,” said Blikstein. “They are powerful learning mechanisms that increase performance by every measure we have.” Pea explained that these results indicate the value for learning of first engaging one’s prior knowledge and intuitions in investigating problems in a learning domain – before being presented with abstracted knowledge. Having first explored how one believes a system works creates a knowledge-building relevance to the text or video that is then presented, he said."
http://blogs.kqed.org/mindshift/2013/07/before-reading-or-watching-videos-students-should-first-experiment/
Reflection
Relevance
Pattern
Emotion
Multi-modal
Experiential
Social
Technological Disruptors
Facebook Story: if someone from the 1950's suddenly appeared, what would be the most difficult thing to explain to them about life today?
I possess a device, in my pocket, that is capable of accessing the entirety of information known to humankind.
And I use it to look at funny videos of cats
The University of Nowhere
‘Place-based colleges’ are good for parties, but are becoming less crucial for learning thanks to the Internet, said the Microsoft founder Bill Gates at a conference on Friday.
Five years from now on the Web for free you’ll be able to find the best lectures in the world. It will be better than any single university,” he argued at the Techonomy conference in Lake Tahoe, Calif. “College, except for the parties, needs to be less place-based.”
from: http://chronicle.com/blogs/wiredcampus/bill-gates-predicts-technology-will-make-place-based-colleges-less-important-in-5-years/26092
MOOC's!
Stanford’s Sebastian Thrun made headlines in the fall of 2011 when his on-line Artificial Intelligence course enrolled over 160,000 students. According to the New York Times (“Harvard and MIT Team Up To Offer On-Line Classes,” May 2, 2012)
Pedagogical Disruptors
Gallup Poll "Big 6"
3% agreed to all 6.
6. Extremely active in extracurricular activities and organizations
5. Internship or job that allowed me to apply my learning
4. Work on a project that took a semester or more to complete
3. A mentor who helped me pursue my goals and dreams
2. Professors who cared about me as a person
1. A professor who excited me about learning
High Impact Learning Practices (AAC&U, 2008)
Immersion experiences
Diversity/global learning
Internships and project-based learning
Undergraduate research
Service learning, community based learning
Collaborative assignments and projects
Learning communities
Instruction vs Learning
Barr and Tagg
Feb. 22, 2011 Christchurch Earthquake
Out of the rubble...
Stasis
Introductions and Overview
Paradigms...
Introductions
More about us
Pairs: what would you like to learn, do, and come away with?
More about me
More about you
Mihi Mihi
Day 2 Workshop Overview
Final Reflections
Assessment and Evaluation of Experiential Education
Facilitating Experiential Education
Day 1 Workshop Overview
Design and Experiential Education
Methodologies of Experiential Education
Defining Experiential Education
Putting Experiential Learning in Context