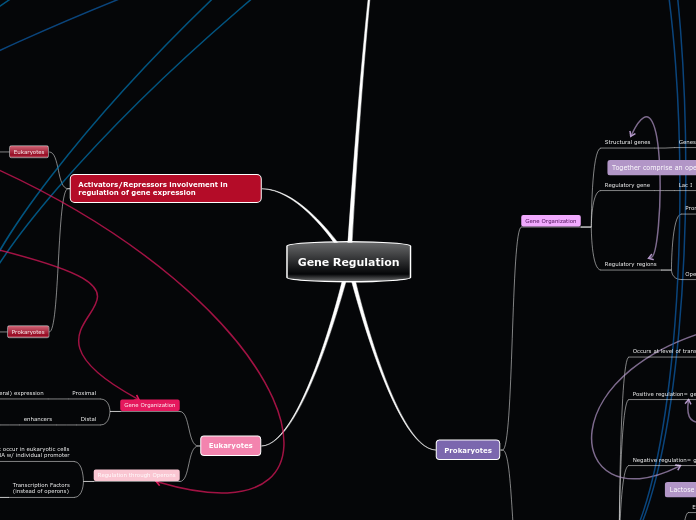
Gene Regulation
Regulation through Operons
Transcription Factors
(instead of operons)
repressors
activators
operons do not occur in eukaryotic cells
- made in mRNA w/ individual promoter
enhancers
bind activator proteins
activator bound to receptor is brought
to promoter via DNA bending proteins
transcription increased via
RNA polymerase II
basal (general) expression
specific to eukaryotes
(ex. humans)
Activators/Repressors involvement in regulation of gene expression
Operons
Helps with regulation with an on-off switch
"Switch"
Negative regulation
Postive regulation
Segment of DNA known as an "operator"
Positioned within promoter
Proteins bind to operators to turn on gene expression for multiple genes
OR to turn off expression
Eukaryotes
Transcription factors
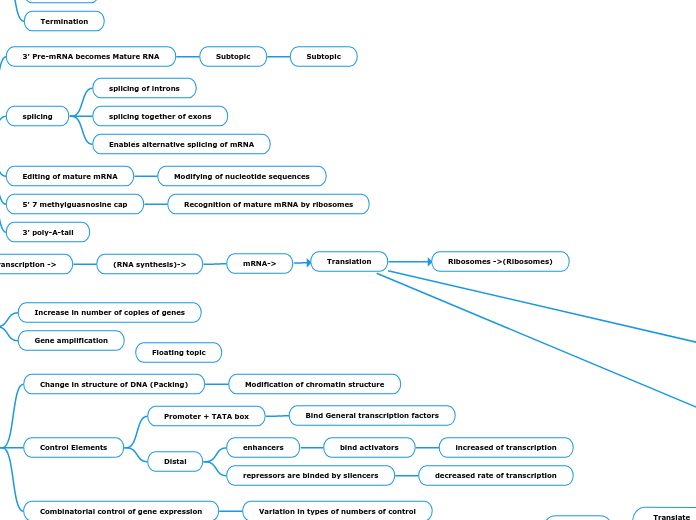
Control elements in DNA
Distal
Bind to specific transcription factors
Can be close or far from gene they are controlling
Sequences in DNA upstream or downstream of gene
Enhancers
Proximal
Bind general transcription factors
Sequences in DNA close to promoter
Specific
Bind to distal control elements called enhancers
Present near or far from gene they are controlling
Change levels of transcription
High levels of transcription are reduced by repressors
Increase levels of transcription
Done by activators
General
Bind to promoter and regions near
Low levels of transcriptions
Background/basal
Proteins that help turn specific genes "on" or "off"
Help increase or decrease level of transcription
Prokaryotes
Regulation Through Operons
Lac Operon
Lactose present, glucose present (cAMP level low)
Presence of Glucose operon OFF
Blocks Adenylyl Cyclase
Prevents production of cAMP
CAP cannot be activated
CAP can't help RNAP to bind promoter
Little lac mRNA synthesized
Lactose present, repressor inactive, operon on
mRNA translates= B-Galactosidase, Permease, Transacetylase
Takes in more Lactose from outside
Break it down to glucose and galactose
Uses sugars as needed
All structural genes are transcribed
Forms a long mRNA
No glucose= operon ON
Inducible operon
Lactose present, glucose scarce (cAMP level high)
Activator protein CAP is activated by cAMP
CAP helps RNAP to bind promoter
Facilitates transcription
Operon ON: Induced/ high expression
Abundant lac mRNA synthesized
Lactose absent, repressor active, operon off
Negative regulation of operon
Transcription of structural genes is blocked
Lac= Lactose
Inducer of the lac operon
Disaccharide made of glucose and galactose
Example of negative and positive regulation
Regulation needs both repressor and operator
Negative regulation= gene expression OFF
Without repressor, transcription occurs
With repressor, no transcription occurs
Repressor protein bond to operator sequence
Positive regulation= gene expression ON
Without activator, no transcription occurs
With activator, transcription occurs
expression at high level
Occurs at level of transcription
Gene Organization
Regulatory regions
Operator
Turn off gene expression
Turn on gene expression
Location where protein binds
The binding causes positive/negative regulation
Proteins are called activators/repressors
“Switch” is a segment of DNA
Promoter
Occurs structural and regulatory gene/s
Regulatory gene
Lac I
Codes for repressor protein
Structural genes
Genes whose expression is controlled together
Lac Z
Structural Gene for B-Galactosidase
Lac Y
Structural Gene for B-Galactoside permease
Lac A
Structural Gene for B-Galactoside transacetylase
Activators/Repressors are
Activated/Made
Far Away from the Gene
Activators bind to mediator proteins
Brings the activator closer to
the promotion site
DNA bending brings activator
closer to promotion site
Activator binds to enhancer
Specific Transcription Factor
Turns gene regulation on or off
Last gene that enters the nucleus
Negative Regulation
Operon Gene Regulation Off
Repressor
Positive Regulation
Operon Gene Regulation On
Activator
Binds to operator
Protein