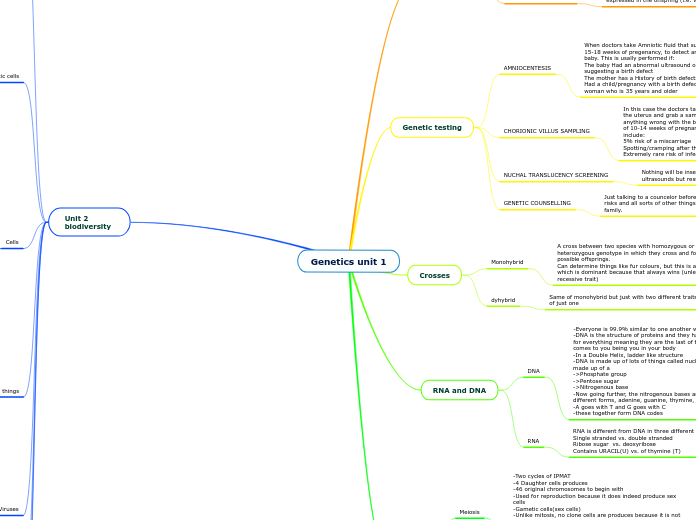
Genetics unit 1
Unit 2 biodiversity
Domains
Kingdoms
Classifying life
Taxonamy
A table that shows the most broad to specific details of an organism
Dichotomous Keys
Yes or no questions to be able to give the reader an easy answer to their organism at hand
Viruses
Antibiotic resistance
This can be caused by the use of drugs in the wrong way where it is harmful. Can be avoided and prevented by using the proper precautions like staying clean
A virus is a non living genetical structure that attacks parts of your body and breaks them down
Structure
Made of DNA, Capsid and tailfiber
Reproduction
Lysogenic cycle
Lytic cycle
The Characteristics of Living things
Able to adapt to an environnement
Able to grow
Able to reproduce
Able to respond to an evironnement
For growth and maintenance, they use energy from proteins and nutrients
Different levels of organization
All are composed of cells
Cells
Eukaryotic
DNA is linear meaning it is full with chromosomes
Can not only reproduce sexually but asexually aswell
Have Membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic
DNA is in a form of a circle
Cannot produce sexually, only asexually
Very old and historical cell
Can cause many sickness'
No Membrane bound organelles
The evolution of Eukaryotic cells
Endosymbiotic Theory
Evidence to prove the theory
Both have similar DNA and ribosomes that show
They have similar insides of the membrane
They reproduce similarly
Popularized by Lynn Sagan in the year 1967, the endosymbiotic theory states that billions of years ago, prokaryotic cells engulfed other prokaryotic cells in which actually formed and created eukaryotic cells
Many of the prokaryotic cell groups actually adapted
These prokaryotic cells started to die off as the oxygen levels of the earth began to rise
Billions upon billions of years ago there was only the cell of prokaryotes
Biodiversity
A lot of human effects on our earth and ecosystems as we produce more and more pollution on a daily basis
Invasive species: Fish that dont belong in bodies of water to bugs in certain arenas, invasive species are disrupting food chains and are killing mainy things like crops and species
Overharvesting: Pushing limits of searching for food and water which is again, hurting our planet
Desertification: The deserts are rapidly expanding causing severe droughts and is causing ecosystems to change or damaged
Deforestation: cutting trees, damaging and detrosying ecosystems on this planet. Causing less co2 to be absorbed
Pollution: CO2 and green house gases are emitted into our atmosphere which is trapping heat from the sun that is reflected by our earth
Important for ecosystems and life on planet earth
Essential for how the world works for the fact it gives us necessities like food, water and clean air
-osis'
Mitosis
-Only one cycle
-IPMAT
-Replicates chromosomes from a single cell and divides them into two identical daughter cells
-Used for places like our skin and liver so that all cells are identical to one another
-Also allows the plants to mass produce leaves with the same cells
-Somatic(body cells)
-Replication occurs in Interphase and also there is a starting amount of 46 chromosomes
Meiosis
-Two cycles of IPMAT
-4 Daughter cells produces
-46 original chromosomes to begin with
-Used for reproduction because it does indeed produce sex cells
-Gametic cells(sex cells)
-Unlike mitosis, no clone cells are produces because it is not repairing anything in the cases
-Some things that make meiosis what it is are thingS like crossing over of the DNA which is from each of the parents cells which includes their DNA, mutations and independent assortment
RNA and DNA
RNA
RNA is different from DNA in three different ways
Single stranded vs. double stranded
Ribose sugar vs. deoxyribose
Contains URACIL(U) vs. of thymine (T)
DNA
-Everyone is 99.9% similar to one another with DNA
-DNA is the structure of proteins and they have the final word for everything meaning they are the last of the last when it comes to you being you in your body
-In a Double Helix, ladder like structure
-DNA is made up of lots of things called nucleotide which is made up of a
->Phosphate group
->Pentose sugar
->Nitrogenous base
-Now going further, the nitrogenous bases and found in four different forms, adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine
-A goes with T and G goes with C
-these together form DNA codes
Crosses
dyhybrid
Same of monohybrid but just with two different traits instead of just one
Monohybrid
A cross between two species with homozygous or heterozygous genotype in which they cross and form 4 possible offsprings.
Can determine things like fur colours, but this is all based of which is dominant because that always wins (unless its a recessive trait)
Genetic testing
GENETIC COUNSELLING
Just talking to a councelor before having a baby. Talks about risks and all sorts of other things based on the history of family.
NUCHAL TRANSLUCENCY SCREENING
Nothing will be inserted into the mother, it is just an ultrasounds but results may differ from those of the first two
CHORIONIC VILLUS SAMPLING
In this case the doctors take a thin plastic the, pass it through the uterus and grab a sample of the placenta to see if there is anything wrong with the baby. Usually offered from the span of 10-14 weeks of pregnancy to women over 35 and the risks include:
5% risk of a miscarriage
Spotting/cramping after the procedure
Extremely rare risk of infection
AMNIOCENTESIS
When doctors take Amniotic fluid that surounds the baby, from 15-18 weeks of pregenancy, to detect anything wrong with the baby. This is usally performed if:
The baby Had an abnormal ultrasound or blood test suggesting a birth defect
The mother has a History of birth defects
Had a child/pregnancy with a birth defect
woman who is 35 years and older
Dominance
Incomplete Dominance
The instance where neither of the parents alleles/traits are expressed in the offspring (i.e. White rose from two pink ones.
CoDominance
The instance where both traits from parents are showed. (I.e. Black and white spots on a bunny)