Governments in Canada
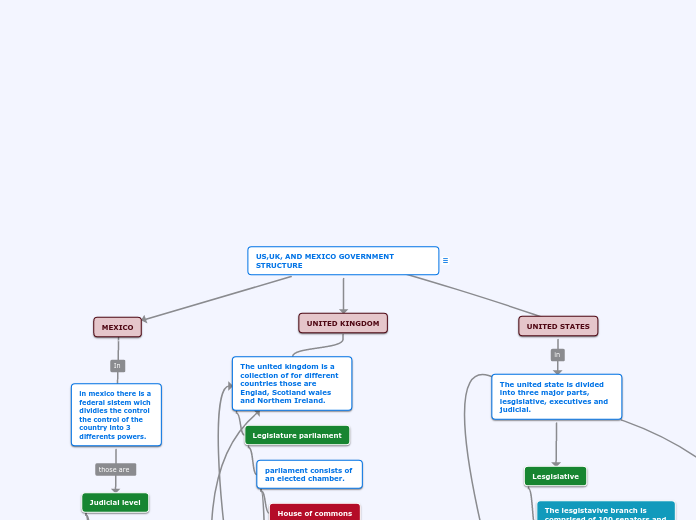
Branches of Government: There are three branches of government in Canada - Legislative, Executive, and Judicial. Together, these branches work together to do law affairs such as making laws, carrying out laws, and evaluating laws.
Judicial
The Judicial Branch, consisting of judges and court, is a branch of government that is responsible for interpreting and applying laws in Canada. The Judicial Branch is independent of the Executive and Legislative Branch. Judges are appointed to a court of justice, where they interpret and apply laws.
Since it is a Judicial Branch and it involves the court, the only people involved in this branch are judges.
Executive
The Executive Branch, commonly known as the Government, is a branch of government that is responsible for decision-making. The Cabinet, chosen by the prime minister, leads the Executive Branch. The prime minister and the Cabinet meet regularly to discuss ideas of new laws, new policies, government spending, and services/programs. The Cabinet Ministers then introduce bills that are questioned, in the House of Commons, by the Opposition.
The people involved in this branch are as follows: Justin Trudeau (Prime Minister), Cabinet Ministers (who are appointed by the Governor General and according to the Prime Minister), and Federal Government departments.
Legislative
The Legislative Branch, or the Parliament, is a branch of government that is responsible for proposing bills and making laws. The people of the Parliament propose bills and introduces them to the Senate or the House of Commons. The bills are debated and voted upon and must be approved by both the Senate and the House of Commons before going to the Governor General, the Queen's representative, to receive his/her Royal Assent. After the Royal Assent is given, the bill has successfully transformed into a law.
The people involved in this branch are as follows: Queen Elizabeth II (Monarch), Mary May Simon (Governor General), Senate (appointed by the Governor General and according to the Prime Minister), House of Commons (democratically elected), and members of Parliament.
Levels of Government: There are three levels of government in Canada - Federal, Provincial, and Municipal. Although each of these three levels have their own jobs and responsibilities, they ultimately work together as a whole to make decisions and deal with laws in all areas in the nation.
Municipal
The Municipal Government is the smallest level of government in Canada and establishes services and by-laws that are administered in the designated town, city, or village. In Richmond Hill, the municipality I currently live in, the building that represents the Municipal Government is the Richmond Hill Mayor & Council building.
The head of the Municipal Government is the mayor or the reeve. Because there are 338 districts in Canada, the name of the mayor/reeve also differs from district to district. The mayor of the city I am currently living in, Richmond Hill, is Dave Barrow
Provincial
The Provincial Government is a level of government that makes decisions relating to laws that directly affect their designated province/territory. Some examples of the responsibilities of this level are as follows: provincial taxes, hospitals, education, marriage, property and civil rights, etc. In Ontario, this level of government meets at Queen's Park, Toronto.
The head of the Provincial Government is the Premier. Although the name of the premier depends on the province/territory, the name of the premier of the province I am currently living in, Ontario, is Doug Ford, who represents the Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario.
Federal
The Federal Government is the highest level of government in Canada and deals with law that affects the nation as a whole. This government not only distributes laws that not only affect Canada itself, but they also deal with international relationships and affairs. Examples of such responsibilities are as follows: national defense, banking, international trading, federal taxes, criminal law, etc. The building in which this level of government meets is Parliament Hill, Ottawa.
The head of the Federal Government of Canada is the Prime Minister. Currently, the prime minister of Canada is Justin Trudeau, who represents the Liberal Party of Canada.