Nv= N exp = (-Qv/KT)
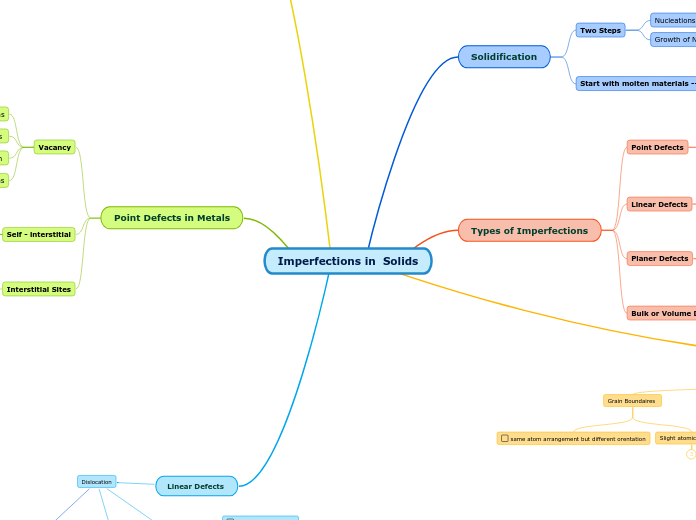
Imperfections in Solids
Linear Defects
Dislocation
Mixed Dislocation
Burgers stay constant
Dislocation alters direction
Move when stresses applied
Permanent Deformation
Edge
Burgers Vecter : b
Shows atom slip, magnitude, and direction
Perpendicular to edge dislocation, parallel to line slip dislocation
Screw
Burgers Vector : b
parallel to screw dislocation
perpendicular to dislocation line slip direction
Form by shear stress
Point Defects in Metals
Interstitial Sites
Both FCC and BCC are octahedral and Tetrahedral
BCC Octahedral :
1/2* 6 + 1/4 *12 = 6 Octahedral sites/cell
6 face-center sites & 12 edges sites
BCC Tetrahedral Sites
24 face sties
4* 1/2* 6 = 12 tetrahedral sites/cells
Self - interstitial
Exist in very small concentrations
Not occur naturally
Found in crystal structures having low packing factor
Host atoms are crowded into interstitial sites
Vacancy
Exchange position with neighboring atoms
Computation of Equilibrium Concentration
Found in all crystalline materials
Result from missing atoms
Impurities in Metals
Solid Solutions
Interstitial solid solutions
Number of atoms remains constant with temperature
max concentration of impurity is < 10%
Impurity latoms smaller than hosts
Extra atoms/ions placed in normally unoccupied positions
Substitutional Solid Solutions
Number of defects is independent of temperatures
Different sizes disturb surronding crystal structures
Replace host ones in lattice sites
Increase the strenght of metallics materials
Metal Alloy
Have enhanced properties
can include multi-phase mixtures
Mixture of a metal and a non-metal
Planer Defecs
Stacking
Occur when errors present in the planer stacking sequence
Found in FCC metal
Twain Boundaries
Found in FCC(annealing) and BCC or HCP(mechanical0
mirror reflections of atoms position across twin planes
Grain Boundaires
Slight atomic Disorder
High Energy State
High Atomic Mobility
High Chemical Reactivy
same atom arrangement but different orentation
Types of Imperfections
Bulk or Volume Defects
Cracks; Pores; Voids; Precipitates; Foreign Inclusions
Introduced during fabrication processes
Planer Defects
Grain Boundaries; Twain Boundaries; Stacking Faults
Boundaries or planes separate a materials into region
Linear Defects
Edge/Screw/Mixed Dislocations
Some atoms are misaligned; Occur along a line only
Point Defects
Vacancies; Interstitial; Atoms; Substitutional; Impurity Atoms
Involves 1 or 2 atomic/ionic positions
Solidification
Start with molten materials --- All liquid
Grain Structure
Crystal growing
Nuclei
Two Steps
Growth of Nuclei
Nucleations