によって Emily Richins 2年前.
95
Knowledge Construction for Mariah
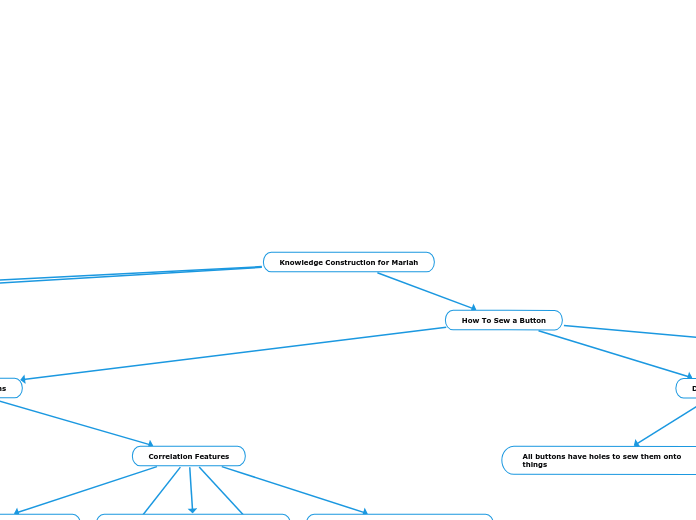
Teaching a young girl how to sew a button involves understanding her developmental stage and using appropriate strategies to ensure effective learning. At the age of seven, she is likely in the preoperational stage according to Piaget, where she begins to use symbols and her language skills are maturing, though she remains egocentric.