LA NOCIÓN DEL SUJETO
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
Fase 7: Tragedia de la existencia
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
Segundo principio de incertidumbre
El sujeto oscila
Y la nada
Alturismo
Para el bien mismo
Entre el todo
Egocentrismo
Subtopic
Por naturaleza
El ~yo~
No es primero porque:
Pero la cultura y el lenguaje le dan las características de la subjetividad a la parte física
La persona nace con el ~yo~
No es puro porque:
Y también el "se"
Siempre incluye el "nosotros"
Primer principio de incertidumbre
El ~yo~ no es primero ni puro
Fase 6: Sujeto cerebral
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
Libertad:
Se divide en:
Condiciones internas
Condiciones externas
La capacidad de elección entre diversas alternativas
El individuo- sujeto puede:
The intensifiers strengthen adverbs adjectives and adverbs and down- toners make them weaker.
tomar conciencia de si mismo a través del instrumento de objetivación que es el lenguaje
Segundo aspecto propio del sujeto humano
Y la cultura
Lenguaje
La afectividad
La subjetividad de las personas actúa por emociones y sentimientos
Relaciona al conocimiento con el comportamiento
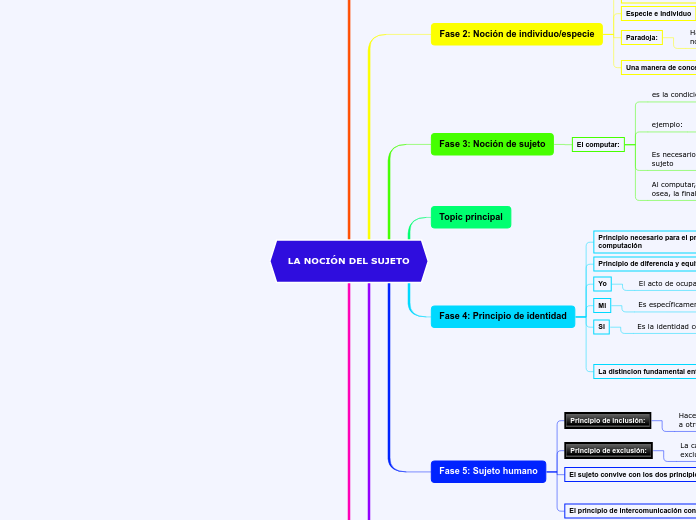
Fase 5: Sujeto humano
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
El principio de intercomunicación con el semejante:
Es una capacidad intrínseca del sujeto de comunicar su subjetividad con sus pares
Deriva del principio de inclusion
El sujeto convive con los dos principios a la vez
Principio de exclusión:
La capacidad del ~yo~ de cada sujeto es única y exclusiva
Principio de inclusión:
Hace que podamos integrar nuestra subjetividad a otros
Fase 4: Principio de identidad
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
La distincion fundamental entre:
Interrogative pronouns are used in questions. Although they are classified as pronouns, it is not easy to see how they replace nouns. Who, which, what, where, and how are all interrogative pronouns.
El yo y el no- yo
El mi y el no-mi
Es
Una distributiva de valor
El si y el no-si
Si
Reciprocal pronouns are used for actions or feelings that are reciprocated. The reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
Es la identidad corporal del sujeto
Mi
A reflexive pronoun ends with ...self or ...selves and refers to another noun or pronoun in the sentence (usually the subject of the sentence). The reflexive pronouns are myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Es específicamente la objetivación del yo
Yo
Demonstrative pronouns are used to demonstrate (or indicate). This, that, these, and those are all demonstrative pronouns.
El acto de ocupación del sitio egocéntrico
Principio de diferencia y equivalencia
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
Principio necesario para el proceso de la computación
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
Topic principal
Fase 3: Noción de sujeto
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
El computar:
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
Al computar, el sujeto es su propia finalidad, osea, la finalidad de si mismo.
También es autoconstitutivo de su propia identidad
Es necesario para la existencia del ser y del sujeto
ejemplo:
Globulos blancos tratando de defender/ eliminar una amenaza externa, ya sea bacterias, virus, etc.
es la condición de posibilidad de supervivencia
Fase 2: Noción de individuo/especie
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Una manera de concebir la paradoja es:
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
Desde el punto de vista del individuo lo es todo, y a su vez no.
Paradoja:
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Hay complementariedad entre esas dos nociones, que no obstante se incluyen entre si.
Especie e individuo
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Nocion de individuo
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
Fase 1: Inroducción al sujeto
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Autocoorganización
Dependencia:
Organizativa
Se organiza gracias a las estructuras del medio exterior
Informativa
Obtiene información del medio
Energética
Alimento
La autoorganización:
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
Se liga a la autonomía
El sujeto se confunde con
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
Considerado del lado de la ciencia
Observamos determinismos :
Sociologicos
Culturales
En esta óptica, el sujeto se disuelve
Fisicos
Biologicos
Lo que consideramos en nosotros superior
La parte divina
Ya que en el radica
La voluntad moral
La libertad
El juicio
El alma
Presenta al mundo como:
Y otro intimo y reflexivo
Relevante al conocimiento cientifico
Subjetividad
Se encuentra en sus rasgos
Manifiesto en forma paradijal
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
Es vidente y a su vez no lo es
La noción del sujeto
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
Extremadamente controvertida