によって Meg Irwin 4年前.
348
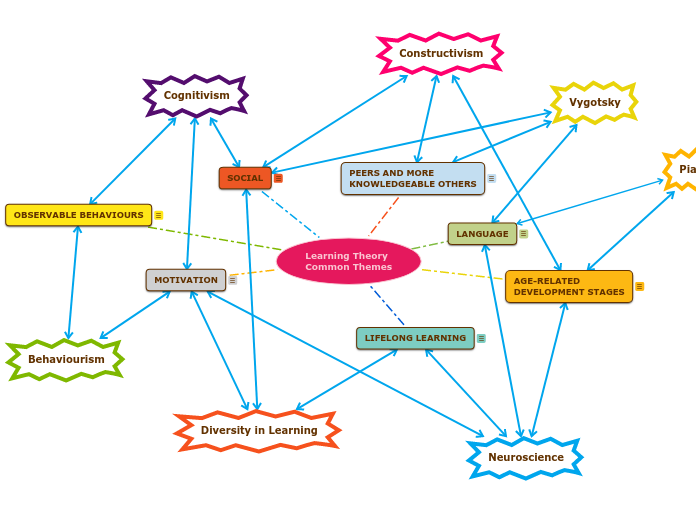
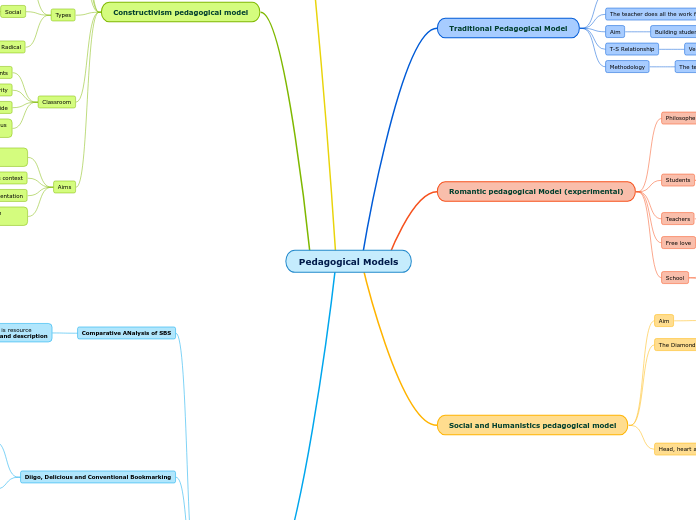
Learning Theory Common Themes
Constructivist learning theory emphasizes the importance of social interactions and collaborative learning. Social cognitive theory highlights the dynamic relationship between social modeling and individual cognitive processes, while Vygotsky’