World War I
CONSEQUENCES OF THE FIRST WORLD WAR
New European States
Economic decline
Material destruction
Death and injury
EUROPE AT THE END OF THE WAR
The organisation of Peace
new conflict
capitalism vs comunism
peace conference
new disputs
leage of nations
international organisation
guarantee peace
but failed
treaty of versailles
signed with germany
powers met at the Paris
peace conference
deice conditions
Population at the economy
US was beneficiary
of the war
european countries
were in debt
agriculture and economy
reduced in size
around 10 million soldiers died
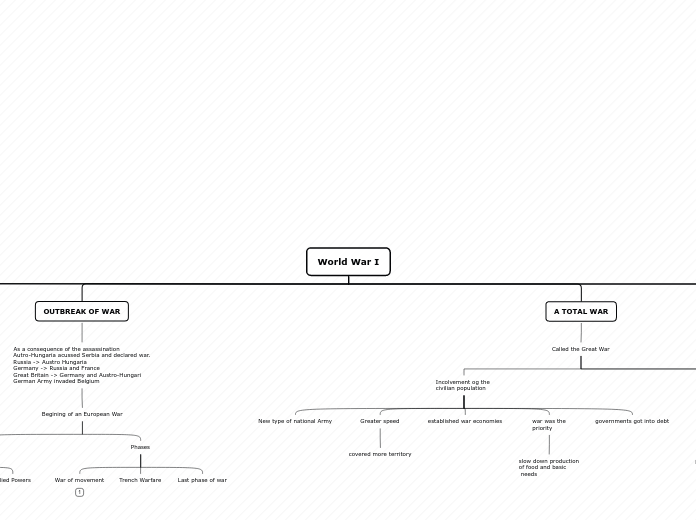
A TOTAL WAR
Called the Great War
The role of women
in the war
new role in society
began working
Propaganda and
opinion control
letters from soldiers
were censored
modern marketing
techniques
propaganda for the war
encouraged pratiotism
Incolvement og the
civilian population
governments got into debt
war was the
priority
slow down production
of food and basic
needs
established war economies
Greater speed
covered more territory
New type of national Army
OUTBREAK OF WAR
As a consequence of the assassination
Autro-Hungaria acussed Serbia and declared war.
Russia -> Austro Hungaria
Germany -> Russia and France
Great Britain -> Germany and Austro-Hungari
German Army invaded Belgium
Begining of an European War
Phases
Last phase of war
Trench Warfare
War of movement
Bahndfajj
Participants
Allied Powers
Central Powers
SHORT TERM CAUSES
Assassination
Conflict between Serbia and Autro-Hungaria
Franz Ferdinand was assassinated
(june 1914)
by a Serbian nationalistic student
LONG TERM CAUSES
Imperialism
A country takes over new lands
or makes them subject to their
rule
Rivalry between Germany
and France and Britain
Nationalism
European powers
Nationalistic
Promotion of national identity
Supporter of the rights
and interests
of one´s country
Most political conflicts
Terriroeial
Alliances
Two opposition alliances
Triple Entente
Triple Alliance
Other countries had no
pition but to declare war
Give each other help
Agreement between
countries
Azpigaia
Militarism
Prepared themselves for war
Fierce competition
Arms race
Arms force
-Army