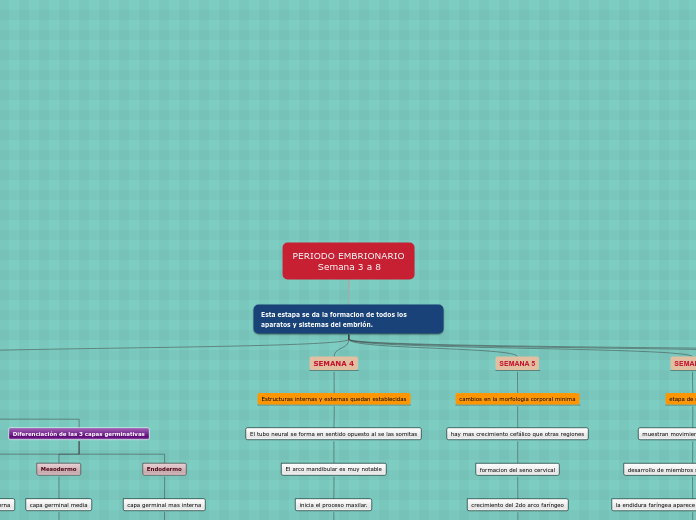
PERIODO EMBRIONARIO
Semana 3 a 8
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
Esta estapa se da la formacion de todos los aparatos y sistemas del embrión.
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
SEMANA 8
final del periodo embrionario
dedos de manos estan separados
visibles los espacios de separacion entre los rayos digitales de los pies
la eminencia cardial esta presente
aparicion del pexo vascular del cuero cabelludo
los primeros movimientos voluntarios de los miembros
la osificaicon primaria se da en los fémures
muestra caracterisitcas claramente humanas
aun la cabeza es grande y constituye la mitad del embrion
formacion de la region cervical y parpados
la diferencia de sexo aun no es clara
SEMANA 7
cambios considerables en los miembros
modificaciones considerables en las extremidades
distincion de los surcos que daran lugar a los dedos
comunicacion entre el intestino primitivo y el saco vitelino, se reduce al tallo vitelino
herniacion umbilical: el intestino se introduce en el celoma extraembrionario
osificacion de los huesos de las extremidades superiores
la formación del pigmento de la retina
SEMANA 6
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
etapa de reflejos
Point of view
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view. Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: I can't get the poetry of the trees,' he said. She nodded. Don't worry,' she said. You will someday. He believed her.' (Paterson, 4. 24)
muestran movimientos espontaneos
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
desarrollo de miembros superiores e inferiores
la endidura faríngea aparece los monticuloa auriculares
el surco neural se convierte en meato acustico externo
los monticulos auriculares contribuyen al oido externo
la cavidad abdominal es pequeña para el intestino
hay mas crecimiento cefálico
SEMANA 5
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
cambios en la morfologia corporal minima
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
hay mas crecimiento cefálico que otras regiones
formacion del seno cervical
crecimiento del 2do arco faríngeo
la cara establece contacto con la prominencia del corazon
funcion exxcretora provicional
SEMANA 4
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
Estructuras internas y externas quedan establecidas
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
El tubo neural se forma en sentido opuesto al se las somitas
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
El arco mandibular es muy notable
inicia el proceso maxilar.
se origina la prominencia cardiaca
se observa 3 arco faríngeos
elevacio destacada debido al prosencefálo
son visibles las placodas óticas
engrosamiento ectodérmicos
eminencia caudal similar a una cola
se establece rudimentos, en especial del sistema cardiovascular
al final de la semana se cierra el neuroporo caudal
SEMANA 3
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
El desarrollo del embrión a partir del disco trilaminar
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Esta estapa se da la formacion de todos los aparatos y sistemas del embrión..
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Diferenciación de las 3 capas germinativas
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of viewSecond person point of viewThird person point of viewOmniscient point of view
Endodermo
capa germinal mas interna
Da origen:
Intestino
Hígado
Páncreas
Pulmones
en la mayor parte de los organos internos
Mesodermo
capa germinal media
Da origen:
Sistema Esquelético
Musculos
Aparato circulatorio
Aparato reproductor
Ectodermo
capa germinal mas externa
Da origen:
Sistema Nervios
Vias respiratorias
Epidermis
Ojos y oídos internos
Tubo digestivo superior
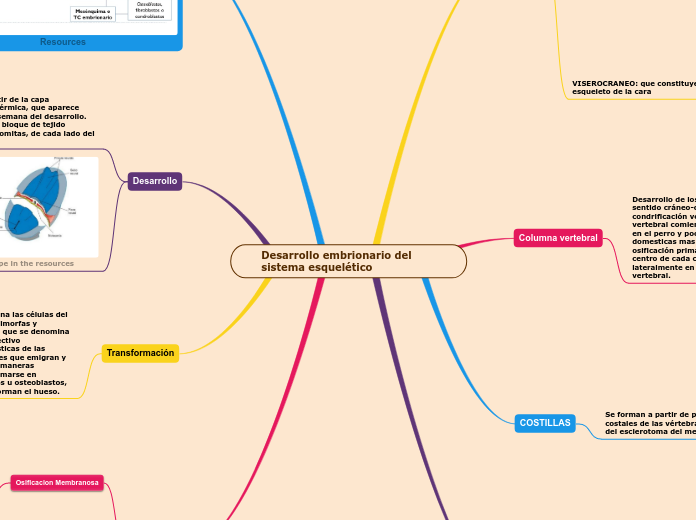
Desarrollo de la Notocorda
celulas mesenquimales se convierte en mesodernmo
las mesenquimales migran cranealmente, formaran el cordon celular
da lugar a la membrana alofaríngea
sube el anmio y la vesicula umbilical
forman areas cardiogénica
la parte proximal persiste como canal neuroenteríco
comunicación entre las cavidades amnióticas y la vesícula umbilical
Aparición de la línea primitiva
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Es el 1er signo morfológico de la Gastrulación
se encuentra en la superficie del epiblasto
Simultaneamente se desarrolla el surco primitivo
Se transforma en mesénquima(formara los tejidos d soporte del embrión
Aumenta la longitud en sus extremos se forma el nodo primitivo y la fosita primitiva
Las células mesenquimales migran
Subtopic