によって BERNAL CONTRERAS BERNAL CONTRERAS 3年前.
383
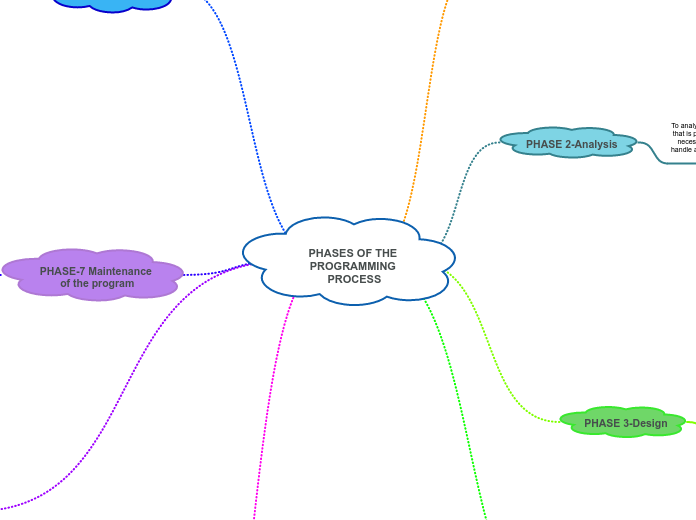
PHASES OF THE PROGRAMMING PROCESS
The programming process encompasses several critical phases, each contributing uniquely to the development and maintenance of software. Initially, the problem is clearly defined to ensure a thorough understanding.