によって Teoh Lee Yuan 4年前.
363
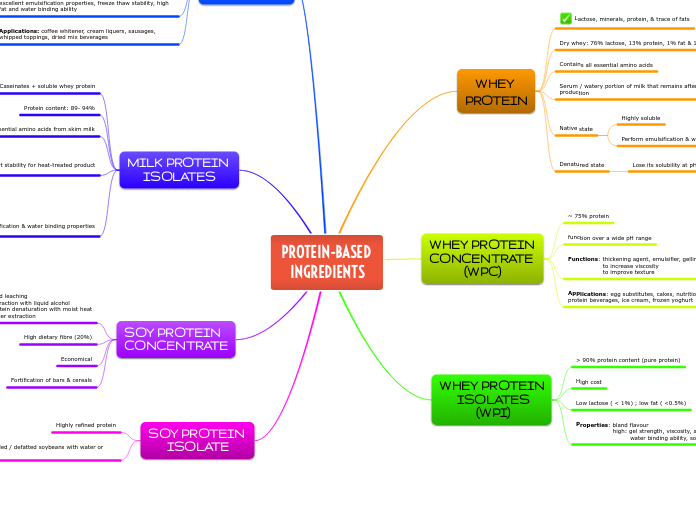
PROTEIN-BASED INGREDIENTS
Protein-based ingredients derived from milk and soybeans are prevalent in various food applications due to their functional properties. Milk protein isolates and caseinates are notable for their high protein content and emulsification capabilities, making them suitable for items such as icings, frozen desserts, and bakery products.