bibliographic reference
Mapios. Resolución 5261 agosto 5 1994. Ministerio de la protección social. Republica de Colombia
consenso de definiciones de vida en cuidados intensivos, asociación Colombiana de medicina critica y cuidado intensivo, federación panamericana ibérica de medicina critica y terapia intensiva. Distribuna 2008.
the clinical status of patients must be evaluated on an ongoing basis to identify which of them no longer need these services
physiological state of the patient has been stabilized or has deteriorated
can be
invasive monitoring requiring immediate intervention
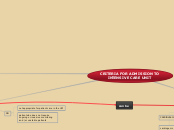
CRITERIA FOR ADMISSION TO INTENSIVE CARE UNIT
Juliette Herrera Cifuentes Paola Godoy
SYSTEMS
ENDOCRINE
diabetic cetoacidosis
severe hypercalcemia
hypernatremia
Gastrointestinal
gastrointestinal bleeding
liver failure
severe acute pancreatitis
NEUROLOGICAL
stroke with impaired consciousness
coma
intracranial hemorrhage
meningitis
infections snc
brain death
RESPIRATORY
Severe respiratory insufficiency
pulmonary embolism
massive hemoptysis
respiratory failure
obstruction by air
CARDIOVASCULAR
cardiogenic shock
arrhythmias
insufficiency
congestive heart
cardiac tamponade
PRIORITY
NO
patient who does not require ongoing or invasive monitoring and / or unstable patients
not appropriate for patient care in the UCI
SI
PRIORITY 3
cardiac tamponade or obstruction of the airway
metastatic malignancies
limits on therapeutic efforts
invasive treatment for acute illness
PRIORITY 2
severe disease
PRIORITY 1
Unstable patients requiring monitoring and intensive treatment
vasoactive drugs
invasive monitoring
circulatory instability
shock
postoperative