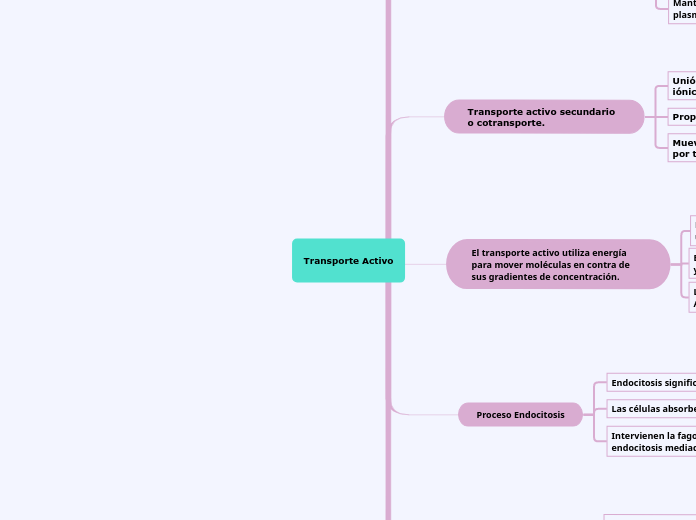
Transporte Activo
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
Proceso Exocitosis
Mecanismo principal por el cual la membrana plasmática aumenta de tamaño.
Una célula expulsa productos de desecho mediante la fusión de una vesícula con la membrana plasmática.
Exocitosis significa "afuera de la célula".
Proceso Endocitosis
Intervienen la fagocitosis, pinocitosis y la endocitosis mediada por un receptor.
Las células absorben partículas o fluidos.
Endocitosis significa "adentro de la célula".
El transporte activo utiliza energía
para mover moléculas en contra de sus gradientes de concentración.
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
La proteína libera el ion y los remanentes de ATP (ADP y P) y se cierra.
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
El ATP cambia la forma de la proteína de transporte y transfiere el ion a través de la membrana.
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
La proteína de transporte
une el ATP y el Ca2�.
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
Transporte activo secundario o cotransporte.
Mueve solutos a través de la membrana por transporte activo indirecto
Proporciona energía indirectamente
Unión del transporte activo con los gradientes
iónicos existentes
Transporte activo primario o Bomba de Na-K (Sodio-Potasio).
Mantiene la separación de cargas a través de la membrana plasmática (potencial de membrana.)
Proteína de transporte específico en la membrana plasmática.
Se encuentra en células animales