Understanding Sustainable Ecosystems
Organisms
Biocontrol
The method of controlling pest organisms, such as insects and weeds, by using other organisms
when animals fight other animals for resources because there’s not enough for everyone.
Biomagnification
Concentrations of toxins in organisms, which comes as a result when these organisms ingest other plants or animals, in which toxins are more widely dispersed
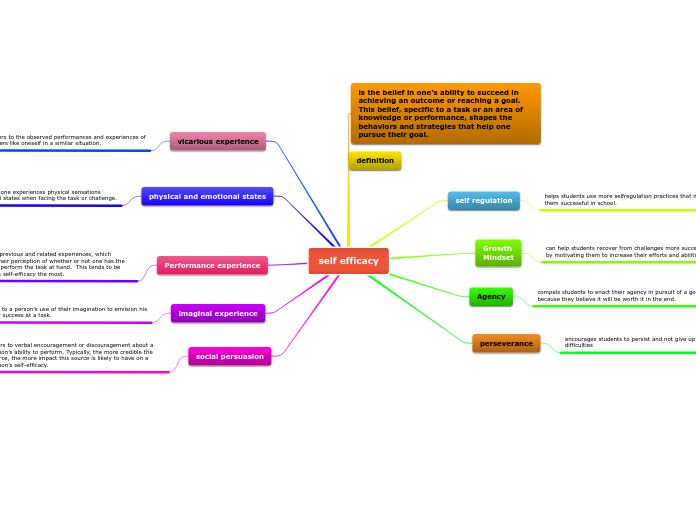
are the living components of an ecosystem. They are sorted into three groups: producers or autotrophs, consumers or heterotrophs, and decomposers or detritivores.
Bioaccumulation
When an organism accumulates chemicals,
such as pesticides
Niche
A niche is the job of an organism .
Predatation
An animal preying On another animal.
Symbiosis
Interaction between two different organisms living in close physical association.
Commensalism
Symbiosis when two different organisms neither gain or lose from each other.
Parasitism
living as a parasite where One party (the parasite) benefits from the second animal while making the second animal feel physical discomfort
Mutualism
Symbiosis beneficial to both animals involved.
Habitat
Reforestation
The restocking of existing woodlands and forests, whether this be from natural, or intentional restocking
Overexploitation
This explains the harvesting of wild species faster than the population can recover.
Bioremediation
To use naturally or man induced microorganisms to break down pollutants in an polluted site and rehabilitate it.
Abiotic Factor
phenomenon that affect the environment but are not alive rain wind snow sleet.
Succession
A number of people or things sharing a specified characteristic and following one after the other
Extirpated
To be rooted out and destroyed completely
Stewardship
Making sure things are sustainable usually involving conversations.
Atmosphere
The atmosphere is a layer of gasses that surrounds the earth
Habitat Loss
Leading to loss of habitat. hings such as urban sprawl, and
pollution are leading to this
the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
Biodiversity
Predation
The act of an animal preying on another animal
Invasive Species
An invasive species is non native to an area and is likely to cause environmental harm to an area.
Captive Breeding
This is the process of raising and maintaining animals
in controlled environments, such as zoos, and other
conservation facilities. These can allow endangered
species to continue to breed safely
Extinct
Species that are extinct simply don't exist anymore, there
are no population of these species left
Endangered
The population of these species are dwindling, thus
they may become extinct in the near future
Alien Species
These organisms are not native to the area they
currently reside in, This can lead to problems, such
as food shortages
Energy
Nutrients
A substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life.
Photosynthesis
This is the manner in which plants get energy through sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
A quantitative property, that has the ability to transfer to an object. Energy can be something as simple as food
Cellular respiration
The process of breaking sugar into a form that the cell can use as energy.
Ecosystem
Limiting Factors
Factors that when subject to even the smallest of changes, can lead to some undeniable change
Exponential Growth
When a growth rate becomes ever more rapid in proportion to the total growing size/number
Sustainable
When something's able to be sustained at a certain level or rate.
Carrying Capacity
The amount of organisms an ecosystem can support
Biotic Factors
These are the living components of an ecosystem. They are sorted into three groups: producers or autotrophs, consumers or heterotrophs, and decomposers or detritivores.
Biosphere
Also known as the ecosphere, is the sum of all essentialed ecosystems worldwide
Aquatic
Aquatic is basically the relationship to water, meaning that if a plant or animal is aquatic it likely lives and thrives in water
Hydrosphere
This is the total volume of water on, under the surface, above the surface, minor planet, or natural satellite
Terrestrial
This type of ecosystem is only found on biomes. There are 6 of these ecosystems. tundra, taiga, temperate deciduous forest, tropical rain forest, grassland , deserts.
Population
Populations show the amount of one species currently residing in an area
Community
Ecological communities are very similar to our own. This term often relates to 2 or more species occupying a given area
Biome
These are very large communities of organisms that reside in certain areas/regions. Organisms may choose to reside in these ares due to the climate.
Food Chain
Competition
When animals fight other animals for resources because there’s not enough for everyone.
Food Web
A system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
Omnivore
Omnivores are organisms that can obtain their energy from consuming both plants, and animals
Carnivore
Carnivores are organisms that obtain their energy for consuming other animals
Herbivore
Herbivores are organisms that obtain all their energy from consuming plants
Trophic Levels
Trophic Efficiency
This explains how efficient energy is transferred from one tropic level, to the next
Tertiary Consumer
These organisms consume Secondary Consumers
Secondary Consumer
These organisms consume Primary Consumers
Primary Consumer
These organisms consume Producers