The Media & Social Problems:
The difference in media consumption between citizens has a big impact on polarization between political parties on certain issues
The media has a big influence on how social problems are defined
There is a high correlation between media consumption and political views
Social problems change over time, as we learn certain issues, the more serious we take them.
The more you understand how research is done, the better you can examine questions.
The study of social problems is always the quality of life of individuals
Knowledge is power: with the more accurate information we have a better chance at solving these problems
Understanding the difficulty involved in fixing: we don’t all agree on what the problem is or the root of the cause. Solving social problems may create other problems
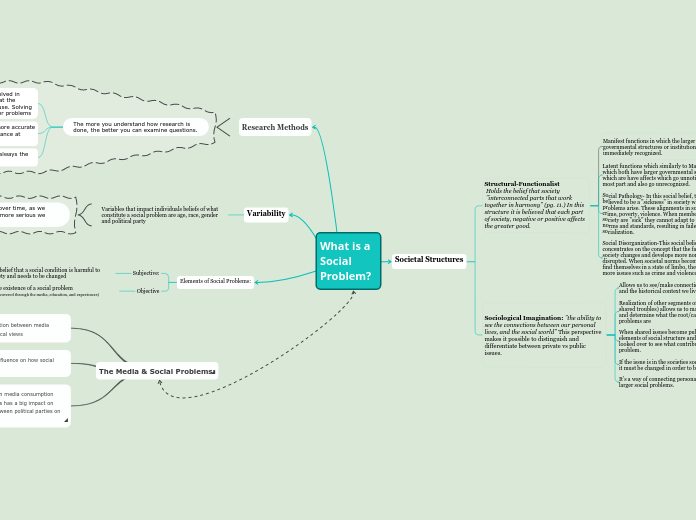
What is a Social Problem?
This template is designed to help you with studying for an exam or qualification. The ideas behind it are described in this article together with tips and suggestions for study techniques.
Begin by typing in the name of the subject that you are studying.
Elements of Social Problems:
The rest of the map (outside the Dashboard and baseline) is for Mind Mapping or Concept Mapping your notes and summaries. If you use multiple maps, make links to them from this one.
Objective
The existence of a social problem (Discovered through the media, education, and experiences)
Subjective:
The belief that a social condition is harmful to society and needs to be changed
Variability
Map out what you already know about this subject. This will help you to connect new learning with previous knowledge.
Variables that impact individuals beliefs of what
constitute a social problem are age, race, gender and political party
Research Methods
Societal Structures
The 'dashboard' topic holds useful information to help organise your studies. It is separate from the notes themselves.
Sociological Imagination: "the ability to see the connections between our personal lives, and the social world" This perspective makes it possible to distinguish and differentiate between private vs public issues.
It's a way of connecting personal challenges to larger social problems.
If the issue is in the societies social structure, then it must be changed in order to be resolved.
When shared issues become public issues, elements of social structure and culture can now be looked over to see what contributed to the problem.
Realization of other segments of society (such as shared troubles) allows us to make connections and determine what the root/cause of these problems are
Allows us to see/make connections with our lives and the historical context we live in.
Structural-Functionalist
Holds the belief that society
"interconnected parts that work together in harmony" (pg. 11.) In this structure it is believed that each part of society, negative or positive affects the greater good.
What are your goals in studying this subject? Are you aiming to pass an exam or gain a qualification? Write it down with target grades if they are important to you.
Social Disorganization-This social belief concentrates on the concept that the faster a society changes and develops more norms are disrupted. When societal norms become weak and find themselves in a state of limbo, the result is more issues such as crime and violence
Social Pathology- In this social belief, there is believed to be a "sickness" in society when social problems arise. These alignments in society include crime, poverty, violence. When members of a society are "sick" they cannot adapt to the social norms and standards, resulting in failed socialization.
Latent functions which similarly to Manifest, which both have larger governmental structures which are have affects which go unnoticed for the most part and also go unrecognized.
Manifest functions in which the larger governmental structures or institutions which are immediately recognized.