by Alexander Refsum Jensenius 1 month ago
190
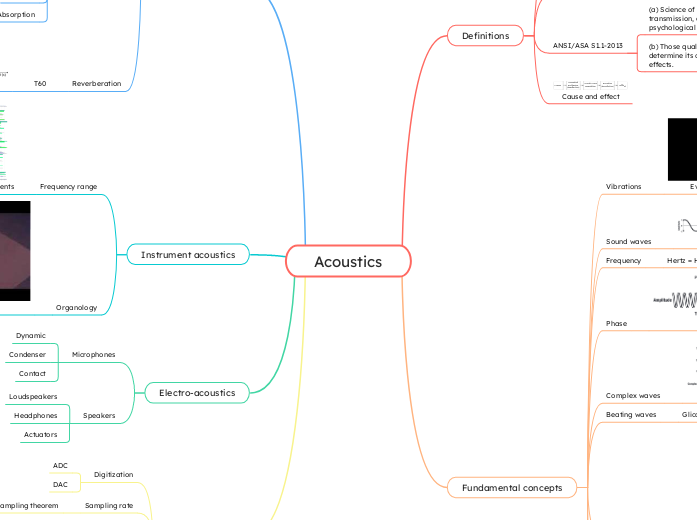
Acoustics
The study of sound encompasses its production, transmission, and effects, which include both biological and psychological impacts. In the realm of acoustics, various fundamental concepts such as frequency, speed of sound, and sound waves play a crucial role.