by Skylar Scott 4 years ago
234
Basics of Art
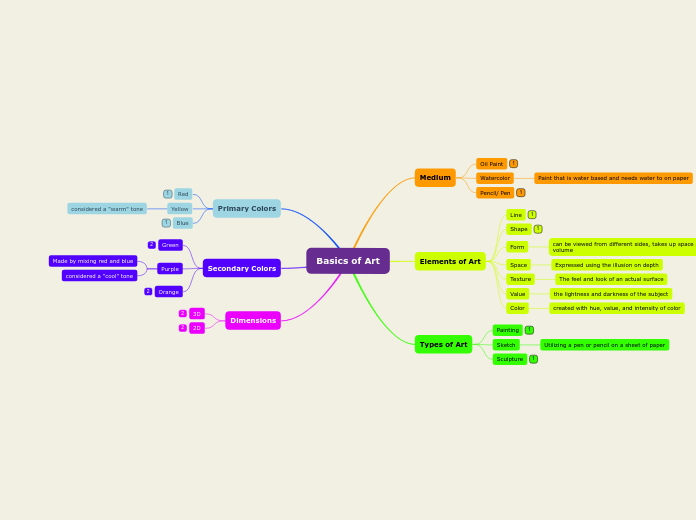
Art comprises various fundamental concepts and techniques that form the basis of artistic creation. Primary colors such as yellow, blue, and red are essential, each associated with warm or cool tones.
by Skylar Scott 4 years ago
234

More like this
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
A preposition is one of the most exciting parts of grammar. A preposition is used to describe the location of something in relation to something else.
A group of words used with the force of a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
When a preposition consists of more than one word, it is called double preposition.
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
When a preposition consists of one word it is called single or simple preposition.
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).