Floating topic
CoA
Pyruvate oxidation
Acetyl CoA
NAD+ to NADH + H+
Autophosphorylation: Each polypeptide takes phosphates from ATP and adds it to the other polypeptide
Both Polypeptides dimerize upon binding of a signal
Termination of Translation
Release Factor
Initiation Complex Dissociates;
Translation Ends
Exit (E) Ribosomal Site
Elongation of Translation
Aminoacyl-tRNA (A) Ribosomal Binding Site
Peptidyl Transferase: Forms peptide bonds between amino acids
3. Amino Acid Chain Formed between P Site and A Site tRNA; chain remains at A Site
Amino Acids added in N-terminus to C-terminus Direction
ce
AMP
Adenylyl Cyclase
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Read from 5' to 3' Direction
Codons
Stop Codons: UAA, UAG, UGA
Sets of 3 Nucleotide Bases
Start Codon: AUG - Methionine
Formyl-Methionine in Bacteria
5' Cap
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Peptidyl-tRNA (P) Ribosomal Binding Site
Anticodons
Single RNA strands of ~80 nucleotides, L-shaped (3D Shape), Clover leaf (2D Shape)
Amino Acids bind to 3' end
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase: Matches a tRNA with its respective amino acid
Unit 3
Transcription, gene expression, RNA processing
RNA Processing
Polyadenylation
adding a poly-A tail at the 3' end of mRNA to export from nucleus
Splicing
removing introns and joining the exrons to produce mature mRNA: spliceosomes
Capping
Adding 5' methylated cap to the 5' end of mRNA to help ribosome bind during translation
synthesized mRNA is ready for translation once transcription is complete
Transcription
Prokaryotes: happens in cytoplasm
Eukaryotes: happens in nucleus
Initiation
RNA polymerase binds to promoter
RNA polymerase II
microRNA
snRNA
pre mRNA
RNA polymerase
Elongation
RNA polymerase II synthesizes pre-mRNA
RNA polymerase moves along DNA template synthesizing RNA (5’ TO 3’)
Termination
RNA polymerase reaches termination and mRNA transcript is released
splicing and addition of a poly-A tail
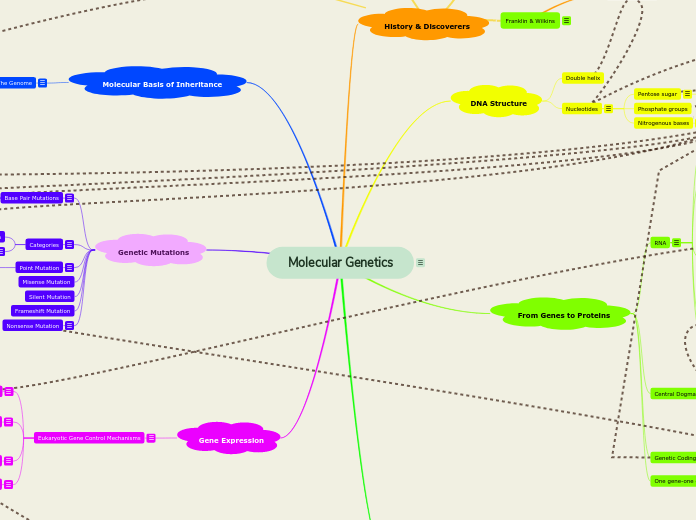
Genetic Information
Pre-mRNA processes into mature mRNA
DNA is a template for RNA synthesis
RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA
Gene expression
Eukaryotes
Enhancers and silencers
They bind to specific regulatory sequences located far from promoter
Prokaryotes
Activators and repressors
bind to specific DNA sequences to regulate transcription
Operons
allows for coordinated expression of genes involved in related functions.
Promoters
Sequences where RNA polymerase binds to a initiate sequence on DNA
Enhancers
Regulatory sequences that increase transcription rate
Repressors
Protein that inhibits transcription by binding to DNA
Activators
Proteins that enhance transcription by binding to enhancer regions
Translation and Protein Transport
Translation
Genetic Code
Nonoverlapping - Nucleotides are read in sets of 3
Degenerate - Multiple Codons code for the same Amino Acid
Universal - Most Organisms Use this to form Proteins
Initiation of Translation
Translation Initiation Complex
Small and Large Ribosomal Subunits
Initiation Factors
Prokaryotes: 70S
Eukaryotes: 80S
rRNA
Protein Transport
Amino Acid Signal Sequences: Chains of Amino Acids that determine a protein's final location in a cell
Endomembrane System Pathways
Destinations (From Free Ribosomes)
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Secretion
Outside Cell
Examples of Secreted Proteins
Digestive Enzymes
Amylase
Extracellular Matrix Proteins
Collagen
Serum Proteins
Albumin
Milk Proteins
Casein
Peptide Hormones
Insulin
Lysosome
Glycoproteins: Carbohydrate groups are added to a protein in the ER by enzymes
SRP
Signal Peptidase: Cleaves SRP Signal Molecule
Organelles
Peroxisomes
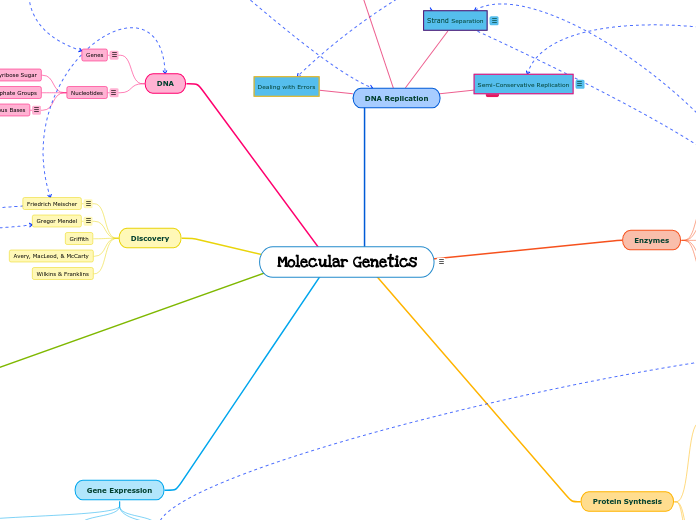
DNA Replication
Prokaryotes: DNA Polymerase III is the main enzyme.
Eukaryotes: Multiple DNA polymerases exist (DNA Polymerase δ for leading strand, DNA Polymerase ε for lagging strand)
Occurs during the S-phase of Interphase
Helicase unwinds the double helix separating different strands of DNA. Breaking the Hydrogen bonds between the two strands.
Single stranded binding proteins keep the
seperated strands apart so that nucleotides
can bind
DNA gyrase moves in advance of helicase
and relieves strain and prevents the DNA
supercoiling again
Each strand of parent DNA is used as
template for the synthesis of the new strands. Synthesis always occurs in 5'-> 3' direction on each new strand.
Leads to formation of okasaki fragments
To synthesise a new strand first an RNA
primer is synthesized on the parent DNA
using RNA primase
Next DNA polymerase III adds the
nucleotides (to the 3' end) added according to the complementary base pairing rules;
adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine.
Nucleotides added are in the form of as
deoxynucleoside triphosphate. Two
phosphate groups are released from each
nucleotide and the energy is used to join the nucleotides in to a growing DNA chain.
DNA polymerase I then removes the RNA
primers and replaces them with DNA
DNA ligase next joins Okazaki fragments on
the lagging strand. Because each new DNA molecule contains
both a parent and newly synthesized strand
DNA replication is said to be semiconservative.
Continuous on the leading strand and discontinuous on the lagging strand.
A semi conservative process that depends on the complimentary base pairs.
Starch
Made of repeating units of alpha glucose connected through 1-4 glycosdic linkages; digestable
Amylopectin: branching
Amylose: no branching
Osmoregulation: the control of solute concentrations and water balance is necessary adaption for life in such environments
Tonicity: the ability of a surroudning solution to case a cell to gain or lose water; generalization
Glycogen
Unit 2
Cell Signaling/Transduction
Signal Transduction
Phosphorylation Cascade
Signal Amplification
cAMP binds to a Protein Kinase, which activates another, and etc...
Cell Response
Forms of Cell Communication
Signal Release
Signal Reception
Stages of Signaling
1. Reception
2. Transduction
3. Response
Binding of a Signal to a Receptor Protein
Receptors
Intracellular Receptors
Steroid Hormone Interaction
Receptor Protein Activated by Binding to Hormone (Ex: Aldosterone)
Activated Hormone-Receptor Complex moves into the Nucleus and activates genes controlling Sodium and Water Flow
Transcription Factor
Signal Molecule is Nonpolar/Hydrophobic and Small; can cross the membrane on its own.
Membrane Receptors
Ion Channel Receptor
Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
Protein Kinase: Enzymes that catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to proteins.
G-Protein Coupled Receptor
G-Protein
Guanosine (Di/Tri)-phosphate (GDP/GTP)
GDP: Deactivates G-Protein
GTP: Activates G-Protein
Phosphatase: Enzyme that catalyze the removal of phosphate groups by hydrolysis
Signal Molecule is Hydrophilic (Charged/Polar); cannot cross a membrane on its own.
First Messenger: Receptor that Receives a hydrophilic signal in the membrane.
Second Messenger: Another molecule that helps the message travel inside the cell
cAMP (Cyclic AMP): Synthesized from ATP
Signal/Ligand
Ex: Aldosterone
Types of Signal Release
Long-Distance Signaling
Local Signaling
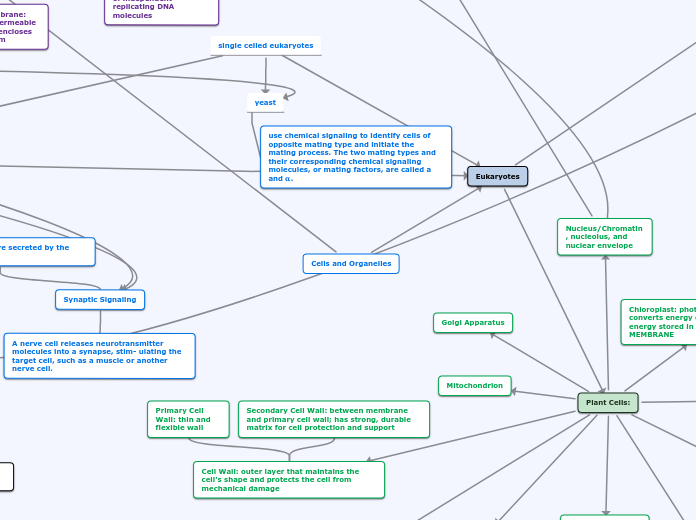
Synaptic Signaling
Neurotransmitters
Post-Synaptic Cell
Presynaptic Neuron
Physical Contact
Energy Flow
Light energy
Photosynthesis in chloroplasts
Light Reactions
Solar to chemical
NADPH
O2
Calvin Cycle
ADP + P
NADP+
Sugar
Organic molecules + O2
Cellular respiration in mitochondria
Glycolysis
Produce pyruvate
Glucose
Glucose 6-phosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate
4 ATP + 2 NADH formed
2 ATP used
CO2 + H2O
Heat
Membranes
Water Balance: Plant Cells
Hypertonic: cell loses water; plasmolyzed
Isotonic: there is no net movement, causing the cell to become flaccid(limp)
normal state is hypotonic solution, cell is turgid(firm)
Electrogenic Pumps: a transport proteins that generates voltage across a membrane protential
H+ Pump: against concetration gradient; ATP based; + charge leaves cell, slight - charge inside cell and + outside cell, whihc creates a concentration gradient
-50 to -200 mV
helps store energy that can be used for cellular work
Membrane Potential
States of the Membrane Potential Cycles
1) Resting State: most Na+ channels closed, and most but not all K+ channels are also closed
2) Depolarization: some Na+ channels open, leading to inflow, depolarizing membrane; if it reaches threshold voltage, action potetnial is trigger and fulfilled
3) Rising Phase: K+ channels remain closed; Na+ influx makes inside of membrane positive
4) Falling Phase: Na+ Channels become inactive; K+ channels open, making inside of cell negative again
5) Undershoot: Na+ Channels close; some K+ channels open; returns to resting state with the help of Na+/K+ pump
Action Potential Graph Components
Repolarization: as the positive charge leaves the cell, inside starts to get less positive
Hyperpolarization: inside of the cell becomes more negative than resting membrane potential
opening of gated K+ channels; INSIDE MORE NEGATIVE
Depolarization: reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential
opening of gated Na+ channels; INSIDE LESS NEGATIVE
Ion channels
Gated: open and close in response to stimuli
Voltage-gated: open/close to change in membrane potential
Ligand-gated: open/close when neurotransmitter binds to channel
Stretch-gated: "sense stretch"; open when mechanically deformed
Ungated: always open
forces exerted on movement of K ions of nerve cells through chemical and electrical forces
any resulting net movement of + or - charge will generate a membrane potential
Water Balance: Animal Cells
normal state is in a isotonic solution
Hypertonic: solute concentration is greater than inside the cell
cell loses water; shriveled
Isotonic: solute concentation same as inside celll no net water movement
Hypotonic: solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell
cell gains water; lysed
Transport Types
Bulk Transport: large molecules like polysaccharides and proteins, cross the memrbane in bulk by vesicles
Endocytosis: taking in something inside cells in bulk
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis: specialized endocytosis that enables the cell to acquire bulk quantities of specfic substances
Pinocytosis: cell takes in extracellular fluid from outside in vesicles
dissolved molecules
Phagocytosis: when a cell engulfs large food particles/other cells by extending part of its membrane out
leads to becoming a food vacuole, digeswted afyer fusing with lysosomes
Exocytosis: transport vesicles migrate to the membrane, fuse, and release their contents
used in secretory cells to export products
Cotransport: coupled trasnport by a membrane protein
occurs when active transport of a solute indirectly drives transport of other substances
Active Transport: movement of substances from low to high concentration; maintains a concentration gradient; uses energy
Example Na+/K+ Pump: abundance of Na+ outside the cell & abundance of K+ inside; to even out, goes against the concentration gradient by 3 Na+ transported out the cell and 2 K+ inside the cell
Passive Transport: diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment
Facilitated Diffusion: passive transport aided by proteins to help diffuse across the membrane
Carried out by channel and carrier proteins
Carrier: undergo a subtle change in the shape that translocates the solute-binding site across the membrane
Channel: provide corridors or channels that allow a specific molecule or ion to cross the membrane
Osmosis: diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane
Diffusion: the tendency for molecules of any substance to spread evenly into the avaliable space as a result of thermal motion; high to low concentration
Chemical Components
Membrane Fluidity
Cholesterol
amphipathic
present in all animal cell membranes
type of Hydrocarbon tail affects fluidity
More Saturated: tightly packed; cannot move as well(viscous)
More Unsaturated: not tightly packed, movement in the membrane
Each Phospholipid has a Specific Phase Transition Temperature
Below Temp: lipids is gel phase & is rigid
Above Temp: lipid is liquid crystalline phase & is fluid
Phospholipid Bilayer
Amphipathic: hydrophobic fatty acid tail and hydrophilic head
Different Types of Bonds: different types of phospholipids due to fatty acids, group attached to phosphate etc.; primarliy noncovalent
Van der Waals
Hydrophilic head due to prescene of phosphate group
Fluid Mosaic Model: describes phospholipids as the fluid component of the membrane while different types of proteins present in this fluid bilayer
Main Components are Lipids and Proteins
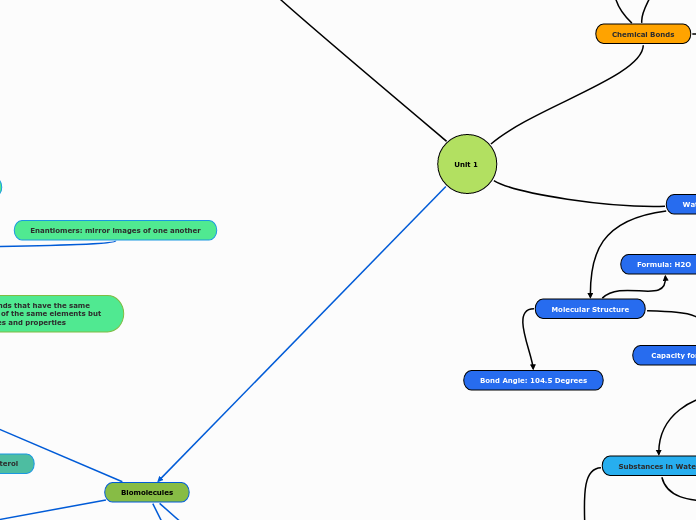
Isomers: compounds that have the same number of atoms of the same elements but different structures and properties
Subtopic
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Carbon fixation
CO2
Photophosphorylation
H2O
Space
Kreb's cycle
Acetyl-CoA
Citrate
Isocitrate
a-Ketoglutarate
Succinyl-CoA
Succinate
Fumarate
Malate
Oxaloacetate
ATP
FADH2
NADH
Synthetic Reaction
Amino acids to Glucose
GTP
Substrate level phosphorylation
Inner membrane
Electron transport chain
Chemiosmosis
movement of H+ down the concentration gradient for ATP synthesis
Unit 1
Cells
Eukaryotic
Eukaya
Membrane-Bound organelles
Both
r
Cytoskeleton
Golgi Apparatus
Nucleus
Mitochondria
ER
Plants only
Vacuoles
Chloroplasts
Animals only
Lysosomes
Prokaryotic
Archaea
No membrane-Bound organelles
Extremophiles
Ether bond in lipids
Circular chromosome
Histones associated DNA
Bacteria
Lack membrane bound orgenelles
Some
Fimbriae, Pili
Endoscope
Flagella
All
Cell wall
Periplasmic space
Nucleoid
Ribosomes
Plasma Membrane
Water Properties
Molecular Structure
Capacity for Hydrogen Bonds
Bond Angle: 104.5 Degrees
Formula: H2O
pH
con
Acids increase Hydronium concentration (More H3O+ or H+ groups).
pH + pOH = 14
Every increase or decrease in pH is a tenfold increase or decrease of the concentration of H+ ions.
Bases decrease Hydronium Concentration (More OH- groups).
Properties of Water
Universal Solvent
Dissolves most substances
Substances in Water
Polar Substances
Polar and Ionic Compounds Dissolve in Water
Nonpolar Substances
Water Forms a Cage Around Nonpolar Molecule
Less Dense as a Solid
Floats on Water; Insulation of Ice for Waters Below
Expansion Upon Freezing
Stable Hydrogen Bonds; Ordered
Most Dense at 4 Degrees Celsius
High Heat of Vaporization
Evaporative Cooling
High Specific Heat
Temperature Moderation
Cohesive Behavior
Water Transport in Plants
High Surface Tension
Chemical Bonds
Intermolecular
van der Waals Interactions
Hydrophobic Interactions
Ion-Dipole Interactions
Hydrogen Bonds
Strong Dipole-Dipole Interactions between H and O, F, or N (Partial Positive H with Partial Negative O, F, N).
Dipole-Dipole
Intramolecular
Ionic Bonds
Crystalline Structures (Salts)
Covalent Bonds
Electronegativity Differences (Greater differences give more polar bonds)
Molecular Function
Size and Shape are key to function.
Biomolecules
Proteins
made of monomers called amino acids
four types of basic groups
Basic (+)
Acidic (-)
Nonpolar
contains H, CH, or carbon ring; hydrophobic
Polar
contains OH, SH, or NH groups
made of main chain and side chain
has a central cabron surrounded by amino, carboxyl, hydrogen, and R group
Nucleic Acids
polymers made of monomers Nucleotides
connected through phosphodiester bonds/linkages through condensation/dehydration reactions
Nucleosides
does not have a phosphate group
nitrogenous base
pyrimidines: C, T(U in RNA)
purines: A, G
phosphate
5 carbon sugar
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
single-stranded
A,G,C,U
Deoxyribonuleic Acid (DNA)
doubled stranded
A, G, C, T
directs synthesis of messenger RNA and control protein synthesis (gene expression)
translation:information from the mRNA is used to make proteins
transcription: information in the DNA is used to make mRNA
provides directions for its own replication
Lipids
Steroids
LDL: low density protein or "bad cholesterol
increased by saturated fats and trans fat
HDL: high density lipoprotein or "good cholesterol"
four fused rings
Fats
Unsaturated
one or more double covalent bonds are found within carbon chain; do not have hydrogen atoms at every position
Trans: trans fatty acids
Cis: presence of double bonds; slight kinks
liquid at room temp
come from plant sources
can contain one tupe of different types of fatty acids
Saturated
increased incidence of cardiovascular disease
no double covalent bonds between carbons; saturated with hydrogen atoms
found in animal sources
solid at room temp
connected through ester linkage
Ester Linkages: connects each fatty acid to an OH in glycerol
compact way for animals to carry their energy stores with them
made of glycerol and three fatty acids
Carbohydrates
Sugars and polymers of sugars
Polysacchrides: formed when 100 or more monosaccharides are bonded together through glycosidic linkages
Structure
Chitin
Cellulose
made of beta-Glucose; no branching; insoluble fiber
Storage
Dextran
Disaccharide: formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides
Glycosidic Linkage: formed through covalent bond
Monosaccharides: simplest sugars; made of C, H, OH, and CO groups
Aldoses: CO groups at the middle of the chain
Ketoses: CO group is in the middle of the chain
Three Types of Isomers
Enantiomers: mirror images of one another
Geometric Isomers
Trans Isomer: opposite side
Cis Isomer: same side
Structural Isomers: differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms