Reproduction of plants
Dispersion
Mechanical
Split lines
Dry
Water
Buoyant
Hard outer cover
Water resistant
Wind
Light
Flat
Winged
Small
animals
Fleshy
Succulent
Sweet Brightly
coloured
Scented
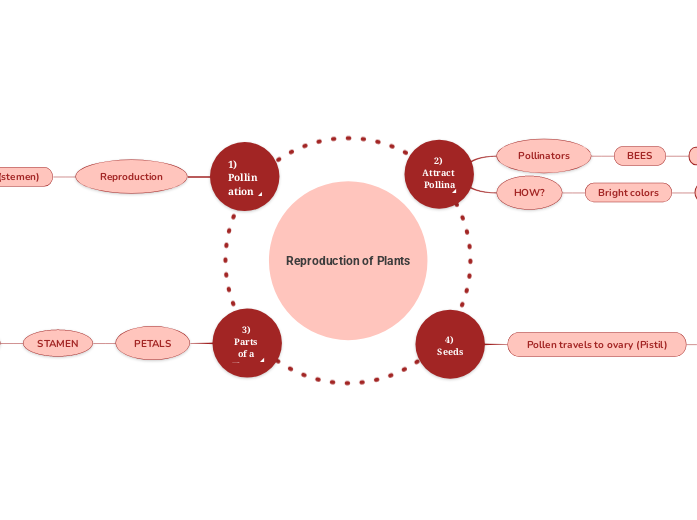
Pollination
Ways of pollination
Wind-polliantion
Insect-pollination
Cross-pollination
pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of a different flower on a different plant of the same species.
Self-polliantion
pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of the same flower or a different flower on the same plant.
Post-fertilisation
After successful pollination, - the ovule develops into the seed - the ovary develops into the fruit
x
Stamen
Filament
Holds anther in optimal position to release pollen grain
Anther
produces pollen grain
split open to release matured pollen grains
Carpel
Stigma
secretes sugary fluids to stimulate growth of pollen grain
Style
holds stigma in optimal position for pollination
Ovary
contains one or more ovules
Sepals
Protects the other parts of the flower during the bud stage