nervous tissue
synapses
post synaptic membrane
synaptic cleft - space between
pre synaptic membrane
neurons
non-myelinated
no myelin sheath
nerve impulse is slower
myelinated
insulated
increased speed
imbalances of chemicals
depression
antidepressant medication makes the neurotransmitters more active for the production
caused by a decrease in production of serotonin
Parkinson's
L-Dopa tablet treatment (pre-curser to dopamine), can pass the BBB, enzymes turn it into dopamine.
caused by a lack of dopamine - body not able to communicate with the brain, causes you to shake
action potentials
depolarise (sodium+ in), repolarise (potassium+ out), hyperpolarise, resting potential
caused by a depolarising current
when a stimuli cause depolarisation past the threshold
an explosion of electrical activity
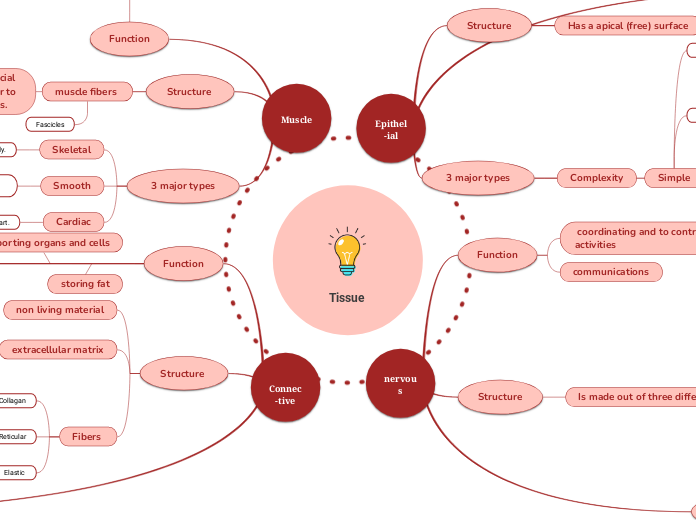
tissue structure and function
twitch muscle
epithelial tissue
found?
skin
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
alveoli
COPD - airway become inflamed, cant get oxygen into tissue, can destroy alveoli
gas exchange
simple squamous epithelium
pseudostratified columnar epithelium in lungs
lining hollow organs
categorisation
squamous, cuboidal, columnar
simple, stratified, pseudostratified. transitional
muscle tissue and fibres
smooth
lines blood vessels
not striated
cardiac
involuntary
1 nucleus per cell
skeletal
mainly voluntary, makes you move
multiple nuclei
striated
endothelial tissue
atherosclerosis
can cause a stroke
lining of the veins and arteries become thicker and harder
plaque
lines veins and arteries
specialized cells
egg cells
first polar body - unwanted chromosomes
zona pellucida - prevents polyspermy
corona radiata - supplies protein
plasma membrane - provides protection
red blood cells
contains haemoglobin
no nucleus
biconcave shape
sperm cells
flagellum - helps with movement
centrioles - detaches head from tail
mitochondria - provides energy
acrosome - releases enzymes to break membrane of egg
root hair cells
contain lots of mitochondria to release energy used for active transport
long root hair for extra surface area to absorb water
white blood cells
monocyte
takes part in immunity
largest
eosinophil
combat particles
bi-lobed
basophil
fights germs
help detect and destroy cancer
lymphocytes
produce antibodies
found in lymph nodes
phagocyte
can move easily to sites of infection
engulfs pathogens and foreign particles
palisade cells
face leaf's upper surface
packed with chloroplast
fit tightly together
adapted to absorb light more efficiently
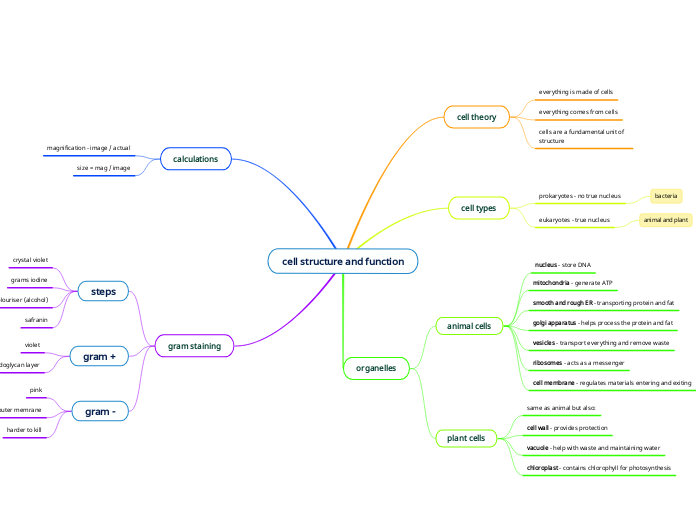
cell structure and function
gram staining
gram -
harder to kill
extra outer memrane
pink
gram +
thicker peptidoglycan layer
violet
steps
safranin
decolouriser (alcohol)
grams iodine
crystal violet
calculations
size = mag / image
magnification - image / actual
organelles
plant cells
chloroplast - contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis
vacuole - help with waste and maintaining water
cell wall - provides protection
same as animal but also:
animal cells
cell membrane - regulates materials entering and exiting
ribosomes - acts as a messenger
vesicles - transport everything and remove waste
golgi apparatus - helps process the protein and fat
smooth and rough ER - transporting protein and fat
mitochondria - generate ATP
nucleus - store DNA
cell types
eukaryotes - true nucleus
animal and plant
prokaryotes - no true nucleus
bacteria
cell theory
cells are a fundamental unit of structure
everything comes from cells
everything is made of cells