by Diana Benavides 4 years ago
366
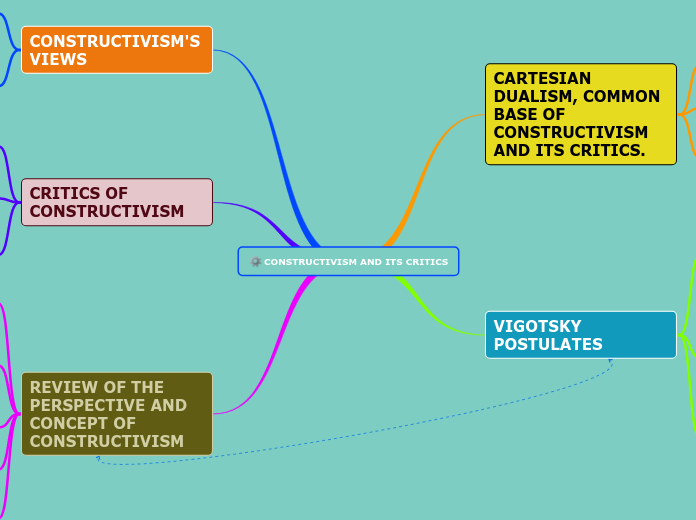
CONSTRUCTIVISM AND ITS CRITICS
Constructivism, as a prominent theory in education, is examined through multiple lenses. Vygotsky's social constructivism and Piaget's cognitive constructivism form the basis of the theory, focusing on the learning environment and individual-centered approaches, respectively.