by Sara Cruise 9 months ago
91
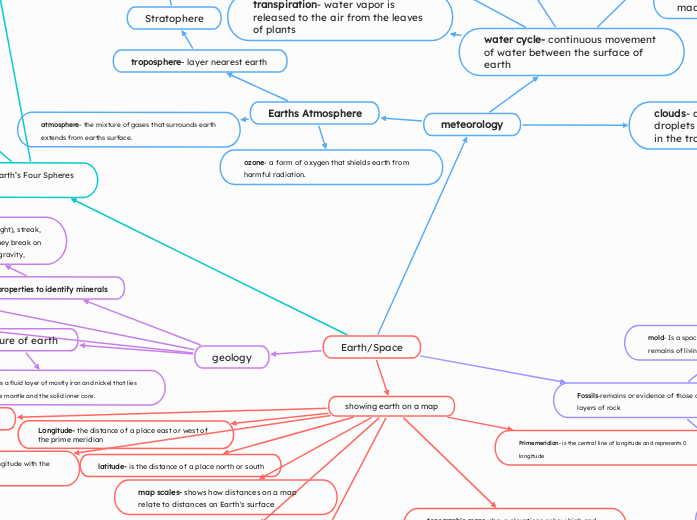
Earth/Space
The Earth's geography is defined by several critical elements such as the equator, prime meridian, and lines of longitude and latitude, which help divide the planet into coordinate systems.
by Sara Cruise 9 months ago
91

More like this
Stratophere
mesosphere
theremosphere
exoshere- outermost layer