Effects of Smoking
Nicotine
nervous system
release adrenaline
affects neurotransmitters in the brain
addictive
reproductive system
babies have low birth weights/ born prematurely/ increase risk of lung problems
increase infertility and miscarriage
prohibits proper blood circulation causing impotence
cardiovascular disease
reduce diameter of arterioles
in oxygen supply
heart rate and blood pressure
aneurysm
stroke
heart attack
cause blood clotting
Carbon Monoxide
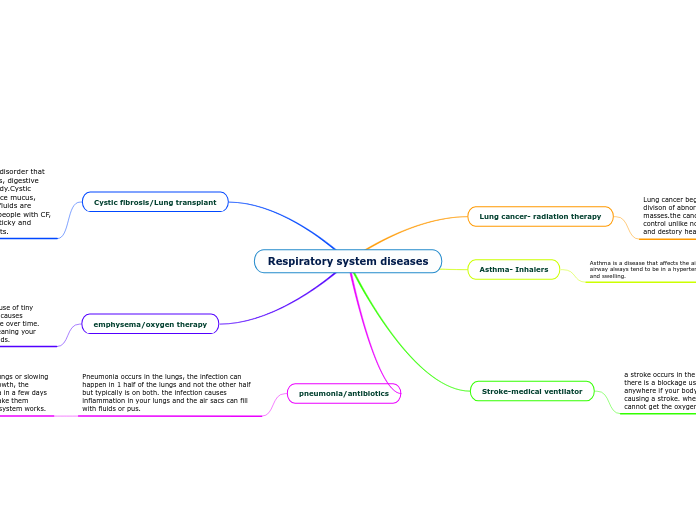
Diseases
Stroke
Coronary heart disease/ atherosclerosis
causes high blood pressure, heart attacks, strokes
hinders blood flow
plaque builds up in arterties
Symptoms
Mimics influenza
fatigue
nausea
vomiting
mental confusion
rapid heart rate
dizziness
headache
Effects
Injure fetus upon exposure
Reduction of blood flow
Build up of fatty tissue
Damage lining of the arteries
Puts a strain on heart muscle
Decreases quantity of oxygen transported in the blood
Mode of action
4. CO is faster at binding with Hb than oxygen and exits the body slower
3. Oxygen cannot bind to receptors on cells that contain carboxyhaemoglobin
2. Combines with haemoglobin to form carboxyhaemoglobin
1. Diffuses into RBC
Tar
Lung Cancer
spread through bronchiole epithelium & enter lymphatic tissue in lungs
react with DNA in epithelial cells to produce mutation & leads to development of tumour
COPD
Emphysema
Emphysema treatment
Long term outlook
Quitting smoking
Alternative therapies
Sulfur has been identified as an aid in reducing inflammation and mucus.
Chinese herbs like ginkgo biloba which helps strengthen the lungs
Surgery and rehabilitation
Some people with emphysema may qualify for surgery to reduce lung volume, which helps to decrease symptoms.
Oxygen supplementation
Oral treatments
Oral steroid like prednisone is prescribed to people in addition to using an inhaler.
Medications as inhalants
Bronchodilators are medications that relax the bronchiolar muscles and improve airflow.
Effects on emphysema
People with severe emphysema often need a continuous supply of oxygen through a face mask.
wheezing occurs and breathlessness becomes progressively worse
Lung function deteriorates
It is a condition in which bronchioles collapse, leaving large spaces where surface area for gaseous exchange used to be
Large spaces appear where alveoli have burst
Less oxygen absorbed to blood
Number of capillaries decreases
Reduces surface area for gas exchange
Protein digesting enzyme known as elastase is released
Destroys elastin in the walls of the alveoli (allowing phagocytes to enter and remove bacteria)
Phagocytes line the airways
Chronic Bronchitis
-accumulation of mucus
difficulty breathing
drowsiness
chest pains
pneumonia
smoker's cough
-cleaning action inhibited
-stimulate goblet cells & mucous glands to secrete more mucous