by Jillian Manchen 3 months ago
62
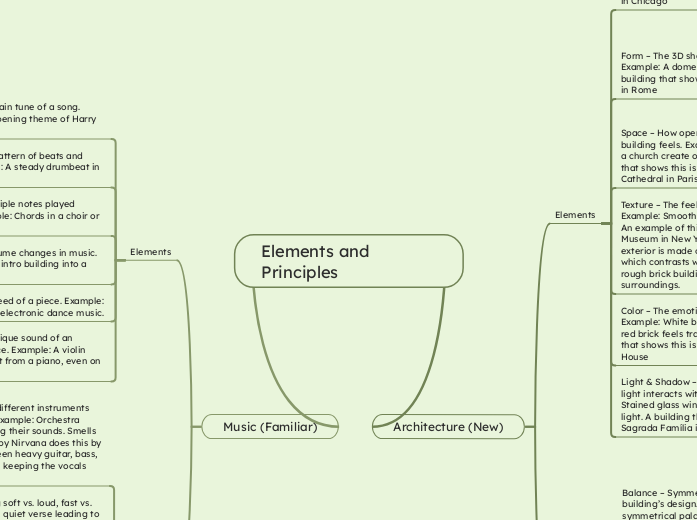
Elements and Principles
In music, the principles of contrast, unity, repetition, and balance play crucial roles in creating engaging and cohesive compositions. Contrast involves the use of varying elements such as soft versus loud or fast versus slow sections, exemplified by songs like Queen'