by Tanveer Singh Marwaha 3 years ago
801
ENGINEERING MATERIALS
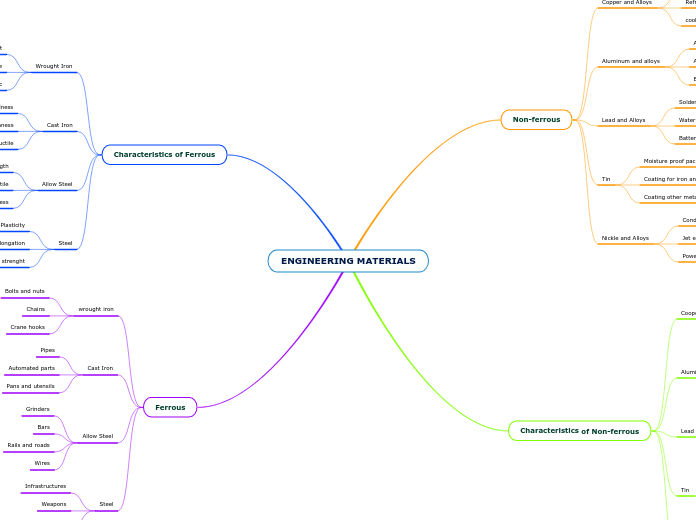
Engineering materials can broadly be categorized into ferrous and non-ferrous types. Ferrous materials include wrought iron, cast iron, and various forms of steel. Wrought iron is known for its magnetic properties and ductility, commonly used for bolts, nuts, and chains.