Evolution
By: Elizabeth Topfer
100592215
Learning Objects:
1. Darwin's Theory
2. Difference between Microevolution & Macroevolution
3. Importance of microevolution to humans
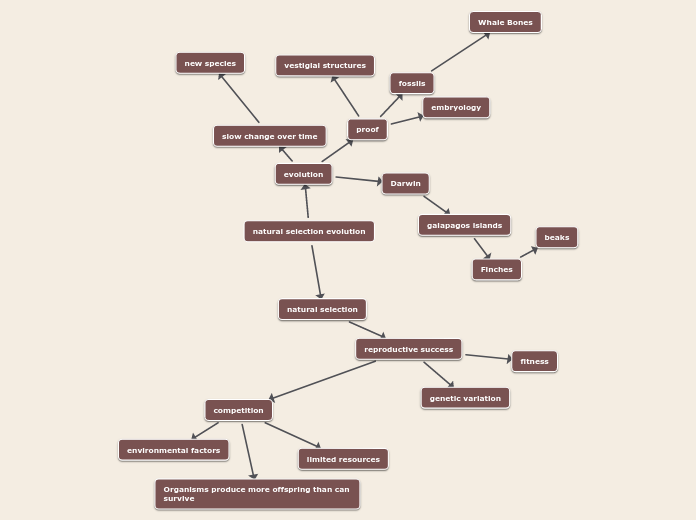
Darwin's Theory (Charles Darwin)
Theory of evolution began in 1800's
Was inspired by this research from travelling the world and noticing different beaks on birds based on their environment.
Darwin's theory of Natural Selection
1. All individuals have a unique combination of genetic traits that are acquired from their parents.
2. The organisms that survive pass on their DNA to their offspring, so closely related individuals have more similar DNA
3. All living organisms over-reproduce, and only some of those offspring will survive, depending on their DNA and the current environmental conditions
4. The organisms that do survive and pass on their DNA provide the basis for future generations to also be able to survive
5. Over time, populations of organisms change because of new combinations of traits in conjunction with changes in the environment
Focused on two main ideas:
Macroevolution
Example:amphibian evolving into a reptile or a reptile evolving into a bird
Definition: The appearance of new species over thousands to millions of years
Difference between Microevolution & Macroevolution
1. Micro-Small biological change
Macro- Large biological change
2. Microevolution- happens through processes such as mutation, selection, gene flow, and genetic drift
Macroevolution- depends on fossil study data
-helps to understand the different organisms and speed of evolutionary changes over time
Importance of microevolution to humans
Artificial Selection
- Humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypical traits
-Mated or cross-pollinated with organisms with similar desired traits
Antibiotic Resistance:
-Importance in health care
-Help fight bacterial infections in people and animals.
Microevolution
Helpful Videos
Example: Long-haired dogs producing a short-haired puppy (NATURAL SELECTION)
Definition: small changes within a single species.