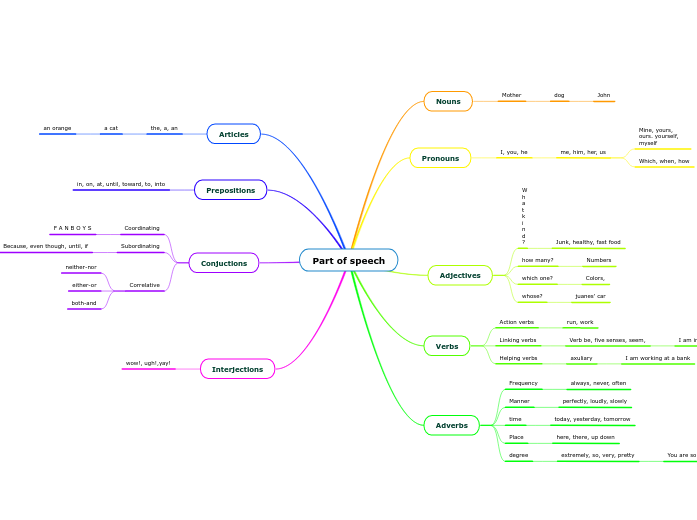
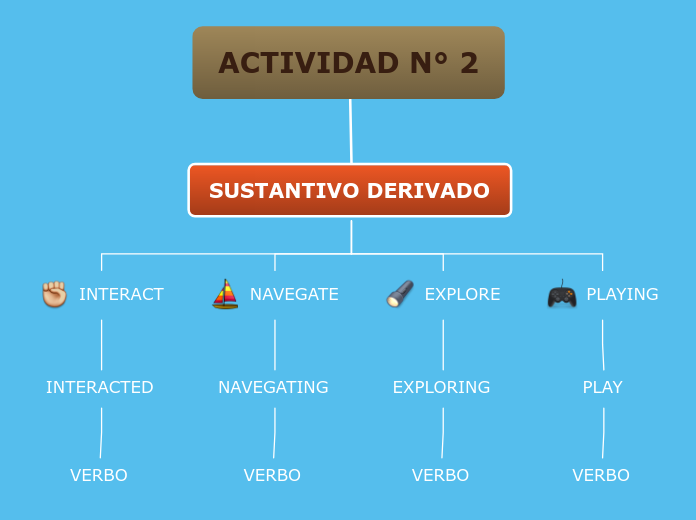
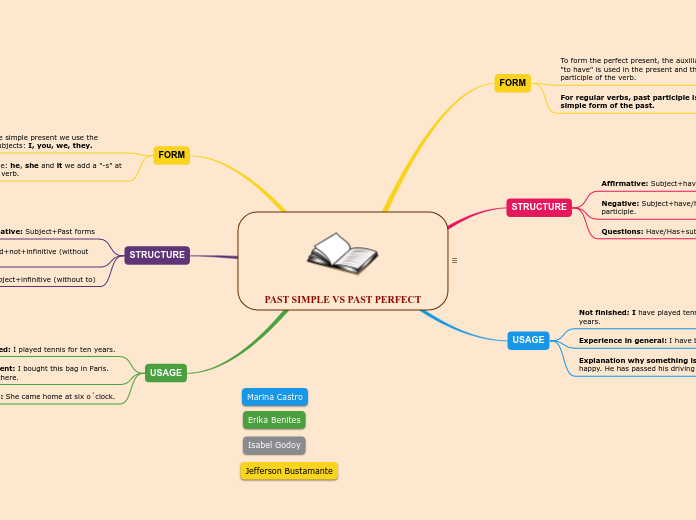
gerund and the infinitive
The gerund and the infinitive are forms of the verbs that act as names. The gerund is formed with "-ing" (walking, eating, etc.) the infinitive is formed with the preposition "to" (to walk, to eat, etc.).
applications
infinitive
To express an objective or why we are doing an action:
After adjectives
I’m here to study English. // I have come to help you
I want to become a teacher.
I’m happy to see you again.
After some verbs like: would like, agree, decide, choose, plan, refuse, hope, want, manage etc.
gerund
When the verb is the subject of the sentence
2.-After a preposition (normally it is about verbs or adjectives with obligatory preposition):
examples
Smoking is dangerous for your health.
I’m interested in learning English. // I’m fond of playing tennis.
He finished doing his homework.
1.-After some verbs: deny, avoid, can not help, like, dislike, enjoy, mind, keep on, suggest, finish etc.