by maddy hopgood 6 years ago
215
Hopgood Maddy legislation
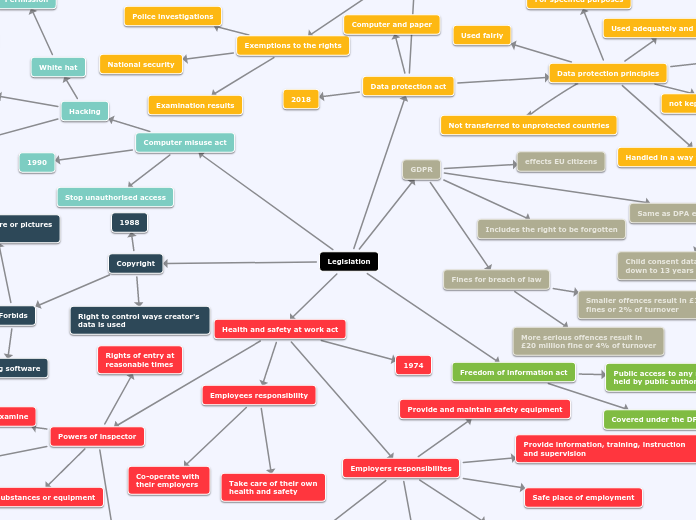
Several laws govern the handling of information and data protection. The Freedom of Information Act grants public access to recorded information held by public authorities, while the Data Protection Act emphasizes the importance of processing data fairly, accurately, and securely, with specific limitations on data retention and transfer.