Important Terms
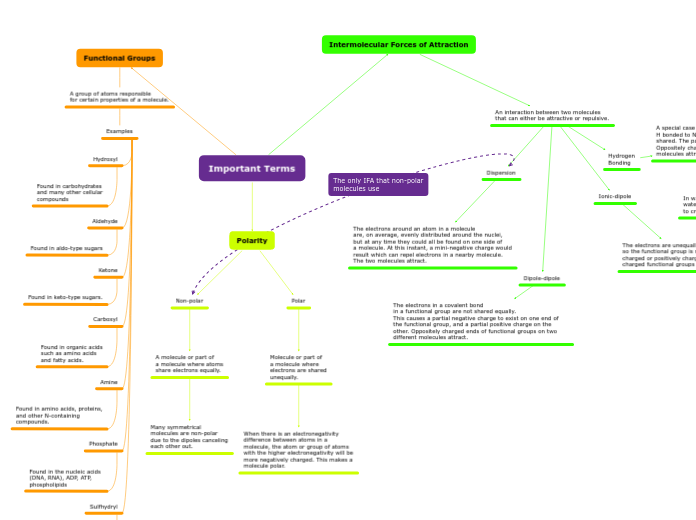
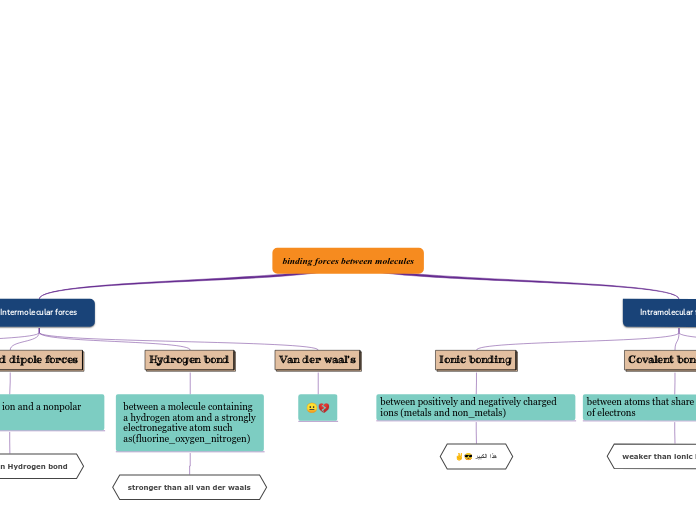
Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
An interaction between two molecules
that can either be attractive or repulsive.
Ionic-dipole
The electrons are unequally shared
so the functional group is negatively
charged or positively charged. Oppositely
charged functional groups attract.
Hydrogen
Bonding
A special case of dipole involving functional groups containing
H bonded to N or O because electrons are more unequally shared. The partial negative and positive charges are stronger. Oppositely charged ends of functional groups on two different molecules attract.
In water, hydrogen in one water molecule connect to another water molecule's oxygen
to create a link of water molecules.
Dipole-dipole
The electrons in a covalent bond
in a functional group are not shared equally.
This causes a partial negative charge to exist on one end of the functional group, and a partial positive charge on the other. Oppositely charged ends of functional groups on two different molecules attract.
Dispersion
The electrons around an atom in a molecule
are, on average, evenly distributed around the nuclei,
but at any time they could all be found on one side of
a molecule. At this instant, a mini-negative charge would
result which can repel electrons in a nearby molecule.
The two molecules attract.
Polarity
Polar
Molecule or part of
a molecule where
electrons are shared
unequally.
When there is an electronegativity
difference between atoms in a
molecule, the atom or group of atoms
with the higher electronegativity will be
more negatively charged. This makes a
molecule polar.
Non-polar
A molecule or part of
a molecule where atoms
share electrons equally.
Many symmetrical
molecules are non-polar
due to the dipoles canceling
each other out.
Functional Groups
A group of atoms responsible
for certain properties of a molecule.
Examples
Sulfhydryl
Found in the amino acid
cysteine and thus
in most proteins
Phosphate
Found in the nucleic acids
(DNA, RNA), ADP, ATP,
phospholipids
Amine
Found in amino acids, proteins,
and other N-containing
compounds.
Carboxyl
Found in organic acids
such as amino acids
and fatty acids.
Ketone
Found in keto-type sugars.
Aldehyde
Found in aldo-type sugars
Hydroxyl
Found in carbohydrates
and many other cellular
compounds