by Buchro Duera-oh 5 years ago
1625
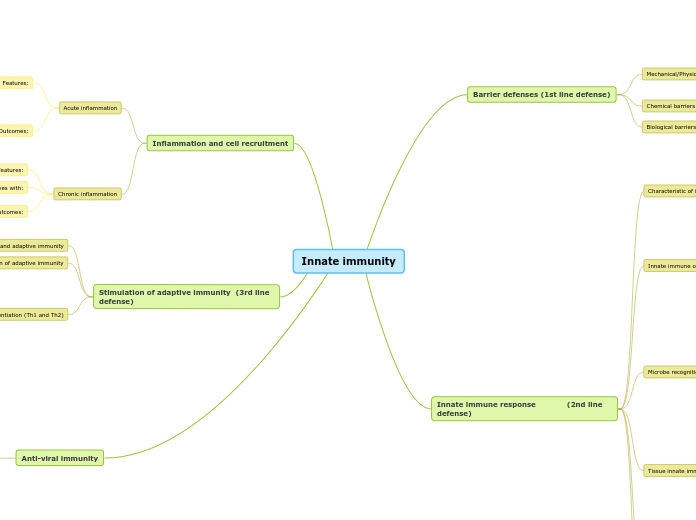
Innate immunity
by Buchro Duera-oh 5 years ago
1625

More like this
• Scarring • Amyloidosis • Neoplasia
Pro-inflammatory(IFN-γ)and anti-inflammatory (IL-4andIL-13)
Prolonged exposure to toxic pathogens
1. Local hemodynamic changes (vasoconstriction → vasodilation) 2. Increase in vascular permeability 3. Extravasation of leukocytes 4. Phagocytosis 5. Outcome of inflammatory response
5 cardinal signs: redness, increased heat, swelling, pain, loss of function
Involves the innate immune system
is involved in host protection against parasite infection and immunopathology in hypersensitivity disease
are professional antigen-presenting cells
are important effector cells in the innate arm of the immune system.
-recognize MHC I -Produce high levels of cytokines
secretes inflammatory cytokines that support immune responses.
an effective first line of defense
are lymphocytes found in the epithelial layer of mammalian mucosal linings
C-type lectin receptors (CLRs)
RIG-like receptors (RLRs)
NOD-like receptors (NLRs)
Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
Endogenous stimuli
Derived from host cells such as tumor cells, dead or dying cells, products released from cells, tissue damage, etc
Exogenous stimuli
Derived from components of microorganisms (pathogens)
is the term used to describe various bacteria and fungi that are permanent residents of certain body sites
tightly joined
preventing microbes from reaching tissues