Linguistics
Deixis
Implicatures
Presuppositions
Speaker
variables
Face
Politeness
Cooperative
principle
Speech act
theory
Sentence vs
utterance
Grammatical vs
Pragmatical
meaning
In context
Context and schema
Force and effect
Inference
Reference
Second Language
Acquisition
Motivation
Integrative
Instrumental
Output
Transfer
Communicative
competence
Strategic
competence
Discourse
competence
Sociolinguistic
competence
Linguistic
competence
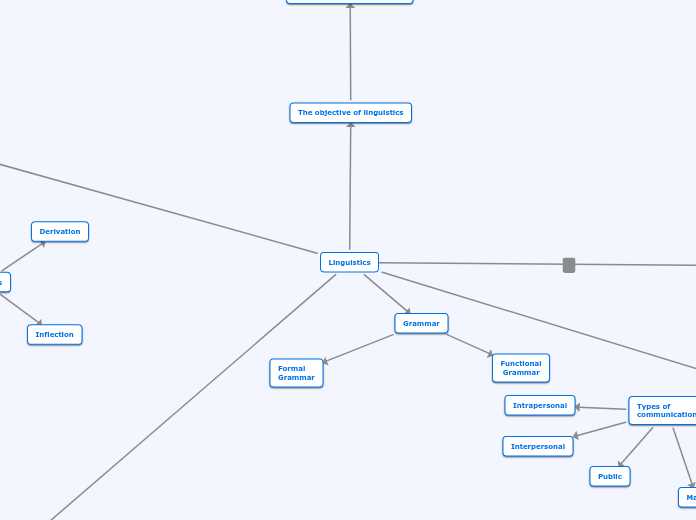
Types of
communication
Mass
Public
Interpersonal
Intrapersonal
Elements of
communication
Context
Noise
Feedback
Channel
Message
Receiver
Sender
Language as a system
of systems
Purposes
Derivation
Morphemes
Morphological
operations
Suprasegmental
change
Ablaut and
suppletion
Reduplication
Affixation
Forms
Allomorphs
Semantic
factors
Conditioned
allomorphy
Phonological
factors
Grammatical
morphemes
Phonetics
Acoustic
Phonetics
Auditory
Phonetics
Articulatory
Phonetics
Suprasegmentals
Stress
Syllable
structure
Intonation
Tone
Length
Writing
transcription
Phonetic
transcription
Phonetic
alphabet
Manners of
articulation
Approximant
Affricate
Fricative
Stop
Consonants
Voiceless
Vowels
Diphthongs
Voiced
Semantics
Intensionality
Tense and
aspect
Modality
Quantifiers
Modifiers
Adverbs/Adverbials
Adjectives
Argument
Predicate
Subject
Concepts
Contradiction
Contradicts
Tautology
Entailment
Ambiguity
Hypernym
Hyponym
Antonym
Synonym
Binding
Theory
Names
Pronouns
Anaphors
Restrictions on
grammar
Movement
Deletion
Recursive
Devices
Coordination
Embedding
Multiple
Adjunction
Grammar:
Modern
Theory
Adjunctions
Complementizer
Inflection
Merger
Projection
Phrase
level
Adverbial
Phrase
Adjective
Phrase
Verb
Phrase
Noun
Phrase
Levels of
structure
Sentence
Clause
Phrase
Word
Adverb
Adjective
Verb
Noun
Grammar
Formal
Grammar
Functional
Grammar
The objective of linguistics
Explanation of the language
depended on a dissociation
of experience.
Language
English as a
global language
Text received
on three levels
Interpretability
Comprehensibility
Intelligibility
Input
Depth
Range
Interlanguage
Circles
Expanding
Outer
Inner
Accent
Variety
Britain
English
American
English
Dialect
Pragmatics
Text
Cohesive
links
Levels of
analysis
Syntax
Lexemes
Morphology
Phonological
Graphological
Syntagmatic
relationship
Paradigmatic
relationship
Types
Tokens
Competence
Communicative
competence
Performance
Parole
Langue