by Kohilavaani Ganesan 7 years ago
705
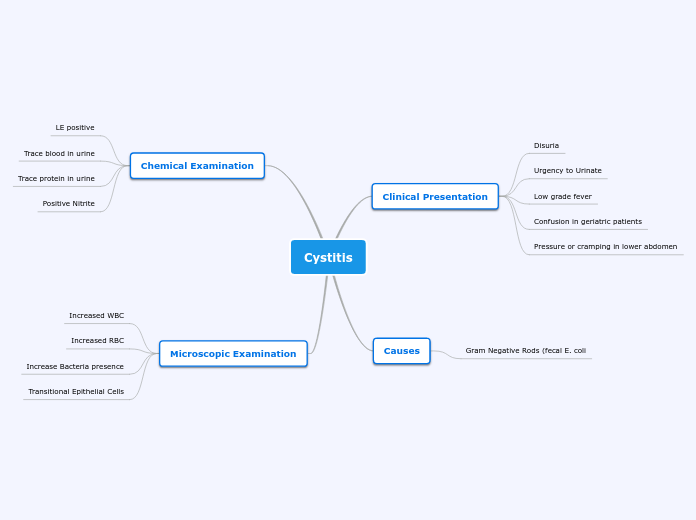
Microscopy Mind Map
The text delves into various microscopy techniques and their applications in studying microorganisms. It highlights the distinction between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria based on cell wall structures, explored through differential staining methods such as acid-fast staining and gram staining.