MTE-280 Investigating Quantity
Rational Numbers
Decimals
Decimals
Example
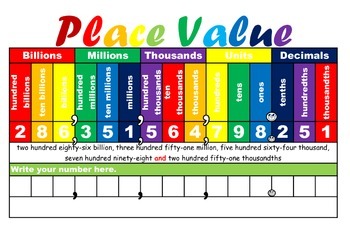
Standard form: 56.85
Expanded Form: 5(10)^1+6(10)^0+8(10)^-1+5(10)^-2
Word form: Fifty six and eighty five hundredths
Fractions
There are three models to represent fractions
- Area model
- Linear model
- Set model
Fraction Language
- The top number(numerator) counts
- The bottom number(denominator) tells whats being counted
When Comparing fractions you can say:
- Same-size parts (same denominator)
- Same number of parts (same numerator)
- More or less than 1
- Closeness to ½ or 1
Equivalent Fractions
Intergers
Concepts
Definition:Integers are a set of numbers that include all the natural numbers (0, 1, 2 ,3 , 4, and so on) and their negatives.
- The opposite of a number is called the additive inverse.
- i.e. 5 opposite is -5.
- Real life Examples: Money, Temperature, Football, Elevation
Methods/Approaches
- Number Line Approach
- Chip Method
Absolute Value: how far away the number is from zero.
- Examples
- -8 absolute value is 8
- Methods
- Number Line
- Chip Method
Ordering Intergers
- Number line is structured so that the numbers increase from left to right
Operations
Addition
Subtraction
Multiplication
- Chip method
- Number line
- Pattern method
Divison
- Chip method
- Number line
- Pattern method
Whole Number Operations
Number theory
Divisibility Rules
- 1- Any whole number is divisible by 1
- 2- If the ones digit is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8 then its divisible by 2
- 3-If the sum of the digits is divisible by 3.
- 4-If the number formed by the last two digits is divisible by 4
- 5- If the ones digit is 0 or 5 then its divisible by 5
- 6- If the number is even and the sum of the digits is divisible by 3.
- 8- If the last three digits formed by the number is divisible by 8.
- 9-If the sum of digits is divisible by 9
- 10-If the ones digit is 0 then its divisible by 10
- 11- If you subtract the even digits by the odd digits formed from the number your difference will be divisible by 11.
Algorithms
Strategies
Properties
Closure Property of Multiplication: If you multiply any two whole numbers the product will be a whole number.
5∗3=15
Commutative Property of Multiplication: Changing the order of the factors won't change the product.
12∗2=2∗12
Associative Property of Multiplication: Changing the grouping of factors doesn't change the product.
(4∗2)1=(2∗1)4
Identity Property of Multiplication: You can multiply any number by one and it keeps its identity.
1∗6=6
Zero Property of Multiplication: When you multiply any number by zero its product will be zero.
0∗8=0
Distributive Property of Multiplication (over Addition): You can multiply a sum of numbers by a number will equal the same as multiplying each number by the number and adding the products.3(8+15)=3∗8+3∗15
Distributive Property of Multiplication (over Subtration): You can multiply the "difference" of numbers by a number and it will equal the same as multiplying each number and subtracting the products.
3(10−2)=3∗10−2∗3
problem types
Problem Types
Addition
- Addition set model
- Addition linear model
Subtraction
- Subtraction takeaway model
- Subtraction missing addend model
- Subtraction comparison model
- Subtraction linear model
Multiplication
- Multiplication:repeated addition set model
- Multiplication repeated addition linear model
- Multiplication area model
Divison
- Partition model
- Measurement model
Numeration Systems
Place Value
Place Value
- Depending on where the digit is placed or positioned defines its value
- The place has a value of 10 times the place to its right
Bases
Bases
Base 10
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
Base 5
1,2,3,4,10
Base 12
1,2,3,,4,5,6,7,8,9,X,E,10
Different Systems
Number Systems
- Hindu-Arabic
- Positional
- Base 10
- Decimal=10
- Used in the United States
- Roman-Numerals
- symbols look like this: IV