by Jenna Scholl 5 years ago
284
Philosophy
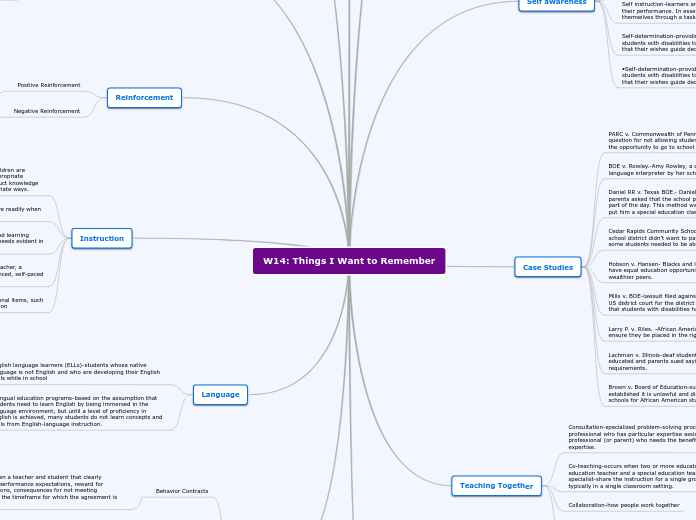
Students learning English as a second language often participate in bilingual education programs, which provide a supportive environment for acquiring English proficiency while simultaneously learning other subjects.