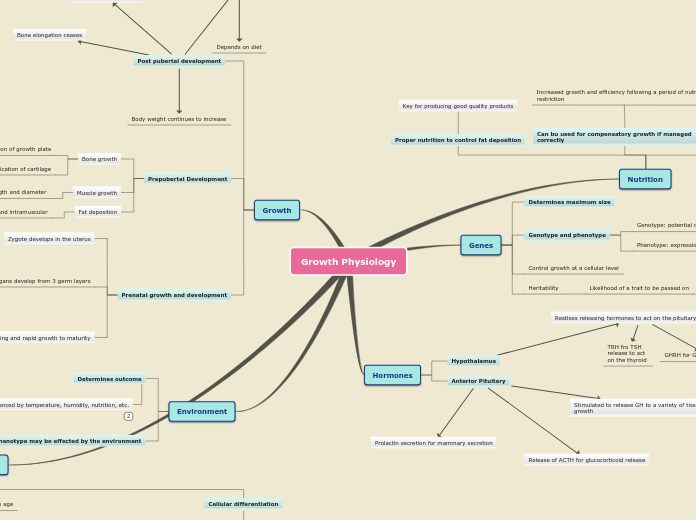
Growth Physiology
Development
Cellular differentiation
Cells differentiate to perform specific functions
Deterioration with age
Decrease in muscle strength and speed
Less elastic collagen
Blood vessels may collapse or bust
Wrinkles
poor reproductive function
Functional Maturation
Change in organ form
Change in organ shape
Environment
Phenotype may be effected by the environment
Determines outcome
Influenced by temperature, humidity, nutrition, etc.
put your mind to work
recall as many details as you can about the keywords you added
Growth
Prenatal growth and development
Hatching and rapid growth to maturity
Bone elongation
All tissues and organs develop from 3 germ layers
Mesoderm
Bones and Muscle
Ectoderm
Nervous system
Endoderm
Lining of digestive tract, pancreas, and lungs,
Zygote develops in the uterus
Prepubertal Development
Fat deposition
Abdominal, subcutaneous, intermuscular and intramuscular
Muscle growth
Muscle fibers increase in length and diameter
Bone growth
ossification of cartilage
extension of growth plate
Post pubertal development
Body weight continues to increase
Bone elongation ceases
Continued fat deposition. Often to increase marbling (intramuscular fat)
Depends on diet
Muscle deposition slows
Hormones
Anterior Pituitary
Stimulated to release GH to a variety of tissues to stimulate growth
Release of ACTH for glucocorticoid release
Prolactin secretion for mammary secretion
Hypothalamus
Restless releasing hormones to act on the pituitary or thyroid
TRH fro TSH release to act on the thyroid
GHRH for GnRh release from AP
Genes
Heritability
Likelihood of a trait to be passed on
Selection for favorable traits such as size and early maturity
Control growth at a cellular level
Genotype and phenotype
Phenotype: expression of that potential
Genotype: potential of animal
Determines maximum size
Nutrition
Effects all stages of development
Can be used to influence time to puberty and/or maturation
Can bu used for compensatory growth if managed correctly
Increased growth and efficiency following a period of nutrient restriction
Proper nutrition to control fat deposition
Key for producing good quality products