Schizophrenia Spectrum & Psychotic disorders
- What is the time period necessary for a person to be diagnosed w/ schizophrenia when displaying positive/negative sxs?
- Six months
- What are the 4 A's associated w/ the negative sxs?
- Alogia, Avolition, Anhedonia, Asociality
- Which dopaminergic tract is associated with prolactin changes?
- Tuberoinfundibular
i
Serotonin System - 5HT Receptors
- present on DA axon and stimulation dec DA release
- 5HT2 r and dopamine r are colocalized
- All antipsychotics have BOTH DA/5HT r binding affinity
- Exception: Pimavanserin for PD psychosis
- NMDA - glutamate sys may be involved w/ psychosis and dec cog.
Tuberoinfundibular pathway
hyperprolactinemia
Nigrostriatal pathway
EPS + tardive dyskinesia
Non-dopamine neurotransmitter systems
NMDA subclass of glutamate receptors
Hypoglutamatergic disorder
Hypodopaminergic activity in mesocortical system
Negative symptoms
Hyperdopaminergic activity in mesolimbic system
Postive symptoms
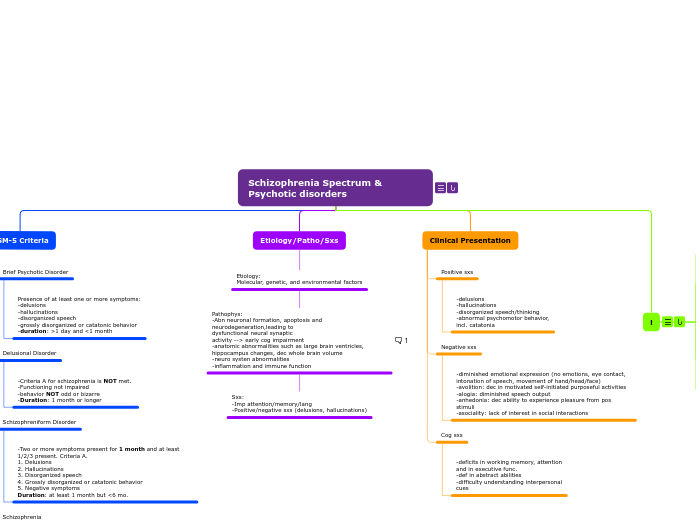
Clinical Presentation
Cog sxs
-deficits in working memory, attention
and in executive func.
-def in abstract abilities
-difficulty understanding interpersonal
cues
Negative sxs
-diminished emotional expression (no emotions, eye contact, intonation of speech, movement of hand/head/face)
-avolition: dec in motivated self-initiated purposeful activities
-alogia: diminished speech output
-anhedonia: dec ability to experience pleasure from pos stimuli
-asociality: lack of interest in social interactions
Positive sxs
-delusions
-hallucinations
-disorganized speech/thinking
-abnormal psychomotor behavior,
incl. catatonia
Etiology/Patho/Sxs
Etiology:
Molecular, genetic, and environmental factors
Pathophys:
-Abn neuronal formation, apoptosis and
neurodegeneration,leading to
dysfunctional neural synaptic
activity --> early cog impairment
-anatomic abnormalities such as large brain ventricles, hippocampus changes, dec whole brain volume
-neuro systen abnormalities
-inflammation and immune function
Inflammation and Immune function:
- overactivation of the immune system --> prenatal infection/postnatal stress
- Overexpression of inflam cytokines --> alteration of brain structure/func
- Insulin resistance and metabolic disturbances
Sxs:
-Imp attention/memory/lang
-Positive/negative sxs (delusions, hallucinations)
DSM-5 Criteria
Schizophrenia
-Two or more symptoms present for 1 month, and at last 1/2/3 present. Criteria A.
1. Delusions
2. Hallucinations
3. Disorganized speech
4. Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
5. Negative symptoms
Duration: cont. disturbance for at least 6 mo.
Schizophreniform Disorder
-Two or more symptoms present for 1 month and at least 1/2/3 present. Criteria A.
1. Delusions
2. Hallucinations
3. Disorganized speech
4. Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
5. Negative symptoms
Duration: at least 1 month but <6 mo.
Delusional Disorder
-Criteria A for schizophrenia is NOT met.
-Functioning not impaired
-behavior NOT odd or bizarre
-Duration: 1 month or longer
Brief Psychotic Disorder
Presence of at least one or more symptoms:
-delusions
-hallucinations
-disorganized speech
-grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
-duration: >1 day and <1 month