Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973
School District Responsibilities Under 504
Educational obligations
Reevaluation
Placement
Neighborhood Schools
Evaluation
Identification
Administrative responsibilities
Developing a system
Training staff regarding their responsibilities under section 504.
Conducting a self-evaluation
Establishing grievance procedures
Ensuring that procedural safeguards are afforded to students and parents.
Notifying the public of a school district’s responsibilities under 504
Appointing a Section 504 coordination
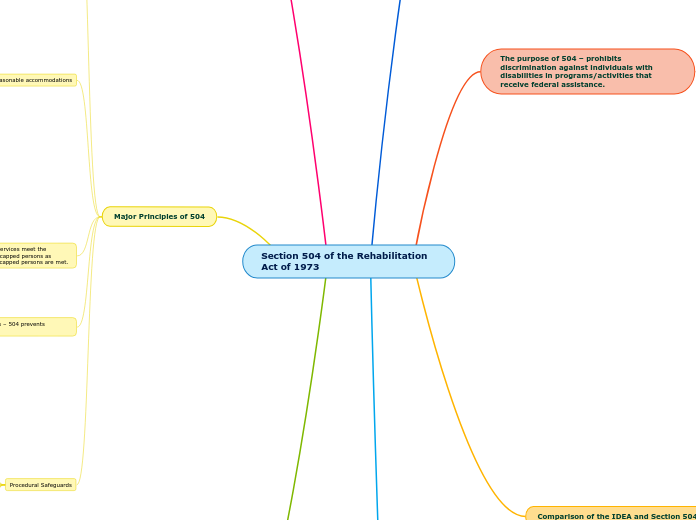
Major Principles of 504
Use mechanisms for resolving disputes including the right to appeal determinations.
Disagree with decisions made by the school.
Give or deny their consent with various decisions the school may make.
Receive prior written notice on matters relating major decisions about your child.
Obtain an evaluation of your child from an outside source.
Participate in meetings that involve your child, especially those where decisions will be made.
We are legally required to respect confidentiality. You have unlimited access to your child’s education records.
Under the Individuals with disabilities Education Act (IDEA), you are presented with various options to support your family members with disabilities. You have a right to receive an explanation of these rights and your ability to challenge IEP decisions.
Evaluation and Placement Procedures – 504 prevents misclassification and misplacement.
Reevaluation must take place prior to a major change in placement.
Be aware of different options for placement based on the individual’s needs.
Process must be documents and all gathered information is considered.
The MDT must draw on information from a variety of sources.
Evaluation must take place before placement.
FAPE – appropriate means aids and services meet the individual educational needs of handicapped persons as adequately as the needs of nonhandicapped persons are met.
Reasonable accommodations
Extracurricular activities – reasonable modifications, aids, and services must be provided to give students with disabilities an equal opportunity.
Avoiding discrimination – alter structure, redesign equipment, reassign classes, assign paraprofessionals, conduct interventions in the gen. ed classroom, modify classroom methods, materials, and procedures.
Access to nonacademic programs and services – equal cost to accessible housing, students with disabilities must have an equal opportunity to participate in athletics, intramurals, and clubs.
In postsecondary education – they cannot inquire if an applicant has a disability, students must self-identify. Admission tests must not discriminate.
Comparable facilities – SPED facilities and services must be comparable to general education facilities and services.
Discrimination v. legitimate considerations – schools may consider a disability when choosing various facilities without being accused of discrimination.
Schools must make sure they do not deny opportunity to participate in or benefit from any program or service available to students without a disability, fail to provide services and aids that are provided to students without disabilities, or provide different aids or services from those provides to students without disabilities (unless those services are required to allow equal opportunity).
In Schools
Modification to examinations to reflect their achievement, not their disability. For example, shortening a test, altering a test format, reducing reading level of test.
Accommodations are needed to ensure that schools do not discriminate. For example, substitution of course, length of time to complete a degree, use of tape recorders, etc.
Court decisions
Not required to send a student to a private residential school if the costs at the private school far exceeded the costs at the public school.
Don’t make new or special programs, just modify the current program.
reasonable accommodations are those that do not impose excessive financial and administrative burdens or require a fundamental alteration in the program.
Protection from discrimination – exclusion or unequal treatment of students with disabilities on the basis of their disability.
Program accessibility – modification or accommodations to programs must be made so students can benefit from them.
Physical accessibility – no qualified handicapped person shall, because a school district’s facilities are inaccessible to or unusable by handicapped persons, be denied the benefits of, be excluded from participation in, or otherwise be subject to discrimination under any program or activity.
SPED 310 wheelchair activity. Things even on BYUI campus need to be updated.
Structure of 504
Subpart G: Procedure (procedures for ensuring compliance)
Subpart F: Health, welfare, and social services (prohibits discrimination in health, welfare, and social services)
Subpart E: Postsecondary education (prohibits discrimination in programs receiving federal assistance
Subpart D: Preschool, elementary, and secondary education (prohibits discrimination in schools)
Subpart C: Program accessibility (accessibility and usability of facilities)
Subpart B: Employment practices (prohibits discrimination in employment)
Subpart A: General provisions (purposes, definitions)
Enforcement of Section 504
Filing for a due process hearing
Filing a complaint with the office of Civil Rights
On-site investigation
Predetermination settlement process
Filing a grievance
Comparison of the IDEA and Section 504
Enforcement
504: Complaints filed to OCR can cut off federal funds, complaints also filed to the state’s department of education.
IDEA: U.S. Office of SPED Programs can cut funds, compliance monitoring by state agency.
Funding
504: No federal funds.
IDEA: Provides assistance of federal funding.
Procedural Safeguards
504: General notice requirements, grievance procedure, impartial due process hearing.
IDEA: Comprehensive and detailed requirements, offers independent testing, no grievance procedure, impartial due process hearing.
Evaluation and Placement
504: Only requires prior written notice, periodic reevaluation, and reevaluation before a big placement change.
IDEA: Requires written consent for both evaluation and placement. Decisions are made as a team. Review IEP progress every year, and reevaluation every 3 years.
LRE
504: Students are always educated in the general education classroom.
IDEA: Students are educated with peers to the maximum extent, but might be removed from the general education classroom when the general education classroom is not successful. There is a continuum from least to most restrictive.
FAPE
504: Offers aids and services on a written education plan to assure equivalency.
IDEA: Services are provided to benefit the student and meet state requirements and are formally written on an IEP.
504: Students must have a mental/physical impairment that affects a major life activity, have a record of such an impairment, or be regarded as having such an impairment. General education and sped students are protected.
IDEA: Student must meet all three prongs of eligibility (adversely affect academic performance, has a disability under the 13 categories, and requires SDI).
Purpose of the Law
504: Civil rights law, protects persons with disabilities from discrimination in all programs that receive federal financial assistance. Accommodations are given to ensure nondiscrimination.
IDEA: Provides federal funding to sates for education of students with disabilities.
The purpose of 504 – prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in programs/activities that receive federal assistance.
Who is protected?
Technically Eligible Students – students with disabilities who are protected from discrimination under section 504 but who do not require services from a school.
Otherwise Qualified
Postsecondary and vocational schools
Elementary and secondary schools
Students are qualified if they are of an age during which nonhandicapped persons are provided such services, of any age during which is it mandatory under state law to provide such services to handicapped persons, or persons to whom the state is required to provide FAPE.
Part 3: A person who is regarded as having such an impairment.
Part 2: A person who has a record of such impairment.
Prevents schools from discriminating.
The person has a physical or mental impairment that does not substantially limit major life activities but is treated by the school as constituting such a limitation, has a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits major life activities only as a result of the attitude of others towards such impairment, or has none of the impairments protected under 504, but is treated by a school as having such impairment.
Part 1: A person who has a physical or mental disability.
Substantial limitation of a major life activity – in addition to a physical or mental impairment, the impairment must substantially limit a major life activity.
Students can be covered, even if their condition is episodic or in remission.
Major life activity: an activity that is typically performed daily.
Substantially: they cannot perform it
Mental impairment – any mental or psychological disorder, such as mental retardation, organic brain syndrome, emotional or mental illness, and SLD.
Are OCD, depression, and Panic disorder are covered? YES!
Disorders learned about in SPED 393: PTSD, schizophrenia.
Physical impairment – any physiological disorder or condition, cosmetic disfigurement, or anatomical loss affecting one or more of the following body systems: neurological, musculoskeletal, special sense organs, respiratory, including speech organs, cardiovascular, reproductive, digestive, Genito-urinary, hemic, and lymphatic, skin, and endocrine.
Even things asthma are covered under 504!
Like the movie, Wonder.
This is NOT special ed. Eligibility for special education is different than creating a 504 plan.
The Development of Section 504: 504 was first created as originally an amendment to a civil rights act, and it was later passed as a revision to the Rehabilitation Act. It has been amended a few times to clarify misconceptions.