DNA sequencing
DNA Cloning
Cloning
Animals
Dolly the lamb
Plants
Totipotent
Stem cell
Embryonic and Adult Stem Cells
Pluripotent
iPS
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Denaturation
Annealing
Extension
Cycle 2
Cycle 3
Gene inserted into plasmid
Plasmid put into bacterial cell
Host cell grown to form clone of cells
Genes used in different ways
Recombinant DNA
Restriction enzyme cuts sugar phosphate backbones
DNA fragment from another source is added
DNA ligase seals the strands
Recombinant Plasmid
Next Generation sequencing
Genomic DNA is fragmented
Fragment isolated
Fragment is copied
Bead placed into a small well to hybidize
In each well, nucleotide is joined
Nucleotide is washed off
Process is repeated
DNA sequence is denatured
Synthesis of new strands
Labeled strands are separated
Thylakoid Space
Stroma
Thylakoids
Chlorophyll
Stomata
Stoma
Mesophyll
Phospholipid Bilayer
Non-Polar
Hydrophobic
Hydrophillic
Photosystems
Linear Electron Flows
Photosystem I
Photosystem II
Electron Transport Chain
Reaction-center complex
Primary Electron Acceptor
Light-Harvesting complex
6CO2 + 12H20 + Light E --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Active Site
Enzymes
Inhibitor
Feedback Inhibition
Allosteric Activation
Cooperativity
Noncompetitive Inhibition
Competitive Inhibition
Normal Binding
Coenzymes
Cofactors
Substrates
Catalysts
Activation Energy
Energy Coupling
Phosphorylated Intermediate
Hydrolysis
Mechanical Work
Transport Work
Chemical Work
Flagella
Second Law
Entropy
Delta G
Delta G = Delta H - T (Delta S)
T: Temperature (K)
Delta H: Enthalpy
Delta S: Change in Entropy
Non-spontaneity
Delta G is Positive
Spontaneity
Delta G is Negative
First Law
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
Acids and Bases
Ocean Acidification
Buffers
PoH
Base
PH
Acid
Scale
1-14
Basic
>7
Neutral
=7
Acidic
<7
Hydroxide Ion (OH-)
Hydrogen Ion (H+)
Floating topic
Chemical Groups
Methyl
-CH3
Phosphate
3 Phosphates
Adenosine
-OPO3 2-
Sulfhydryl
-SH
Amino
-NH2
Carboxyl
-COOH
Carbonyl
>C=O
Hydroxyl
-OH
Molecules
Nonpolar Molecule
Polar Molecule
Organic Molecules
Variation
Enantiomers
Cis - Trans Isomers
Structural Isomers
CHONPS
Molecular Shape/Function
Double Bond
Triple Bond
Single Bond
Bonds
Atomic Mass
Atomic Number
Atomic Nucleus
Matter
Elements
Carbon
Hydrocarbons
Carbon Skeletons
Rings
Double Bond Position
Branching
Length
6 Electrons
Isotopes
Radioactive Isotopes
Atoms
Neutrons
Electrons
Electron Orbitals
Up to 8 Electrons
Valence Electron/Shells
Chemical Bonds
Chemical Reactions
Metabolic Pathway
Anabolic
Catabolic
Make Bonds
Break Bonds
Van Der Waals
Hydrogen Bonds
Reason Ice Floats on Water
Adhesion
Cohesion
Surface Tension
Water
Solvent
Solution
Solute
Aqueous Solution
Subtopic
Heat of Vaporization
Evaporative Cooling
High Specific Heat
Temperature
Heat
Calorie
Ionic Bond
Anions
Cations
Covalent Bonds
Attraction: Electronegativity
Nonpolar
Polar
s, p, d, f
Lose Energy
Absorb Energy
Energy
Laws of Energy
Thermodynamics
Chemical Energy
Thermal Energy
Kinetic Energy
Potential Energy
Energy Levels of Electrons
Free Energy
Endergonic
Exergonic
Protons
Ex) Copper
Trace Elements
Essential elements
Compounds
Ex) NaCl
Cell
Transportation
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Potassium Pump
Homologous Chromosomes
Sodium Pump
Division
Sister Chromatids
Meiosis
Telophase 1
Anaphase 1
Metaphase 1
Prometaphase 1
Prophase 1
Mitosis
Metaphase
Centromeres
Telophase
Anaphase
Cell Plate
Cleavage Furrow
Prometaphase
Centrosomes
Prophase
Kinetochore
Communication
Signaling Molecule
Growth hormone
Epinephrine
First Messengers
Cell Junction
Gap Junctions
Tight Junctions
Plasmodesmata
Signaling Hormones
Receiving Cell
Receptors
Local Signal
Synapse
Long Distance Signaling
Blood Vessel
Signal Transduction pathway
Receptor tyrosine kinases
Tyrosines
Dimerization
Phosphorylation Cascade
Kinsaes
Protein Kinase A
Protein Kinase
Transcription factor
Cellular Response
Growth
Apoptosis
Phosphotases
G-Protein Coupled receptor
Protein
Cytoplasm
cAMP
Phosphodiesterase
Second messengers
G-Protein
GDP
GTP
Components
Biological Molecules
Carbohydrates
polysaccharide
Storage Polysaccharides
Cellulose
Glycogen
Starch
Amylopectin
Amylose
disaccharide
lactose
monosaccharide
glucose
Nucleic Acids
nucleosides
Pentose sugar
Deoxyribose
Ribose
RNA
rRNA
nucleotides
Nitrogeneous base
ACGTU
Phosphate groups
Proteins
Types
Integral Proteins
Trans-membrane Proteins
Aquaporins
Transport Proteins
Amino Acids
Primary Structure
Secondary Structure
Tertiary Structure
Quaternary Structure
Beta sheet
Alpha helix
Lipids
Fatty acids
Unsaturated
Saturated
Plant Cells
Photosynthesis
Calvin Cycle
Phases
Regeneration
G3P
Cycle 3 Times
Sugar
Carbon Fixation
CO2
Carbohydrate
Light Reactions
O2
Photophosphorylation
ADP
Solar Energy to Chemical Energy
Nature of Sunlight
Electromagnetic energy
Electromagnetic Wavelengths
Wavelengths
Action Specrum
Photons
Excited State
Cyclic Electron Flow
Fluorescence
Electromagnetic Radiation
Visible Light
Light Receptors
Pigments
Accessory Pigments
Carotenoids
Photoprotection
Reflect
Absorb
Absorption Spectrum
Chlorophyll b
Chlorophyll a
Spectrophotometer
Electromagnetic Spectrum
NADP+
NADPH
Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Splits H2O
Electron Carrier
Electroins
NADH
Pyruvate
Pyruvate Oxidation
Citric Acid Cycle/ Krebs cycle
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ATP
Chemeiosmosis
Net 36-38 ATP per Glucose
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
ATP Synthase
Cytochrome C
Ubiquinone
Complex 4
Complex 3
Complex 2
Complex 1
Proton Pumps
H+
FADH2
Acetyl CoA
Gluucose
Aerobic Respiration
Anaerobic Respiration
Cytosol
Fermentation
Alcohol
Ethanol
Yeast
Lactice Acid
Muscle Cells
Redox Reactions
Reduction
Oxidation
Isotonic
Turgid
Flaccid
Plasmolyzed
Animal Cells
Shriveled
Normal
Lysed
Structure
Mitochondrial Matrix
Granum
Mitochondria
Inner Membrane
Inter-membrane Space
Cell Membrane
Cell Capsule
Nucleoid
Chromosomal DNA
Pilus
Chloroplast
Thylakoid Membrane
Microvilli
Vacoule
Plasma Membrane
Cytoskeleton
Microtubles
Intermediate Filaments
Microfilaments
Cell Wall
Organelles
Centrosome
Peroxisome
Lysosomes
Apparatus
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth ER
Rough ER
Nucleus
Chromatin
Nuclear Envelope
Nucleolus
Nuclear Membrane
Nuclear Pores
DNA
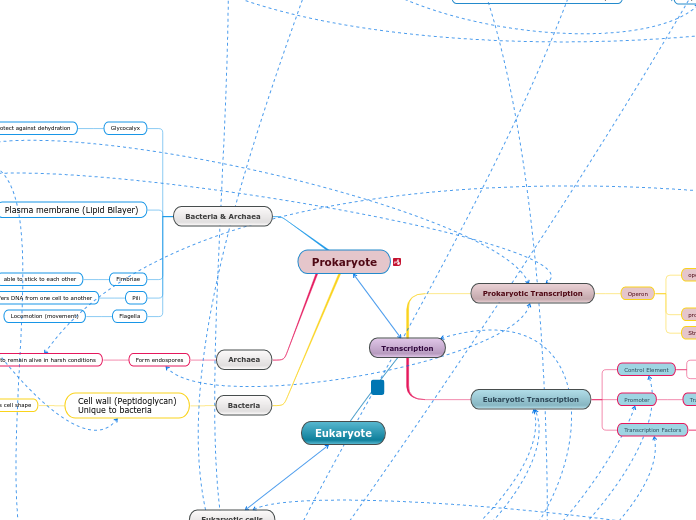
Transcription
Initiation
Downstream
Upstream
Promoter
Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes
RNA polymerase III
RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase I
Translation
Ribosomes
small subunit
large subunit
binding sites
polypeptide
mRNA binding site
Exit site
Aminoacyl site
Peptidyl site
tRNA
amino acid
anticodon
upstream
promoter
RNA polymerase
RNA transcript
poly-A tail
5' cap
pre-mRNA
Intron splicing
mRNA
Nucleotides