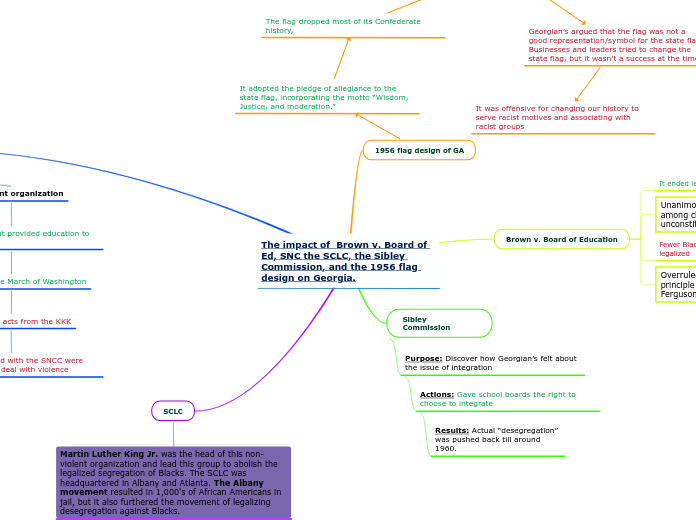
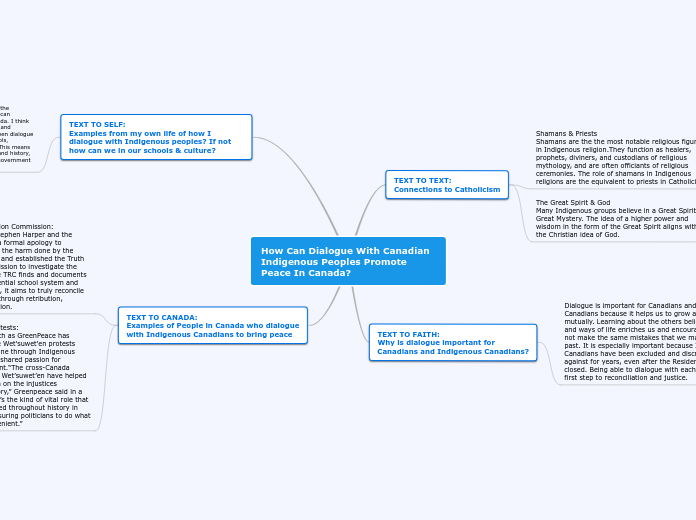
The impact of Brown v. Board of Ed, SNC the SCLC, the Sibley Commission, and the 1956 flag design on Georgia.
SCLC
Martin Luther King Jr. was the head of this non-violent organization and lead this group to abolish the legalized segregation of Blacks. The SCLC was headquartered in Albany and Atlanta. The Albany movement resulted in 1,000's of African Americans in jail, but it also furthered the movement of legalizing desegregation against Blacks.
Included marches, efforts to register black voters, and boycotts of segregated businesses
Provided assistance to small, local groups interested in protesting for civil rights in their towns.
Many people were jailed and possibly (could've been) killed/violated by their acts because it angered many whites that they were fighting for Blacks rights. Ex. Rosa Parks refused to give up her seat on the bus and was put in jail for her actions.
SNCC
Non-violent organization
Freedom schools that provided education to young blacks
Participated in the March of Washington
Faced violent acts from the KKK
Many people involved with the SNCC were arrested and had to deal with violence
John Lewis coordinated the campaigns in which registered blacks to vote and getting college students to engage in the campaigns.
Sibley Commission
Purpose: Discover how Georgian’s felt about the issue of integration
Actions: Gave school boards the right to choose to integrate
Results: Actual “desegregation” was pushed back till around 1960.
Brown v. Board of Education
Overruled the "separate but equal" principle set forth in the 1896 Plessy v. Ferguson case.
Fewer Black businesses owned after this was legalized
Unanimous vote that racial segregation among children in public schools was unconstitutional
It ended legal segregation
1956 flag design of GA
It adopted the pledge of allegiance to the state flag, incorporating the motto “Wisdom, Justice, and moderation.”
The flag dropped most of its Confederate history,
As a response to the Supreme Court rulings on desegregating schools, the Georgia state flag was changed Feb. 13, 1956, incorporating a Confederate battle symbol.
Georgian’s argued that the flag was not a good representation/symbol for the state flag. Businesses and leaders tried to change the state flag, but it wasn’t a success at the time.
It was offensive for changing our history to serve racist motives and associating with racist groups